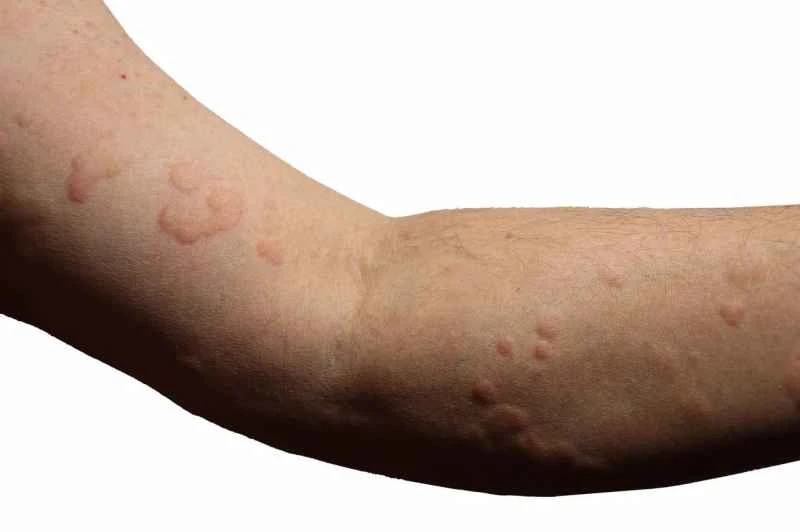
Treatment for urticaria usually requires selecting appropriate medication based on specific symptoms and under the guidance of a doctor. Commonly used medications include antihistamines and corticosteroids, but the specific medication used should be determined based on individual circumstances, and it is recommended to use them after a doctor's diagnosis.
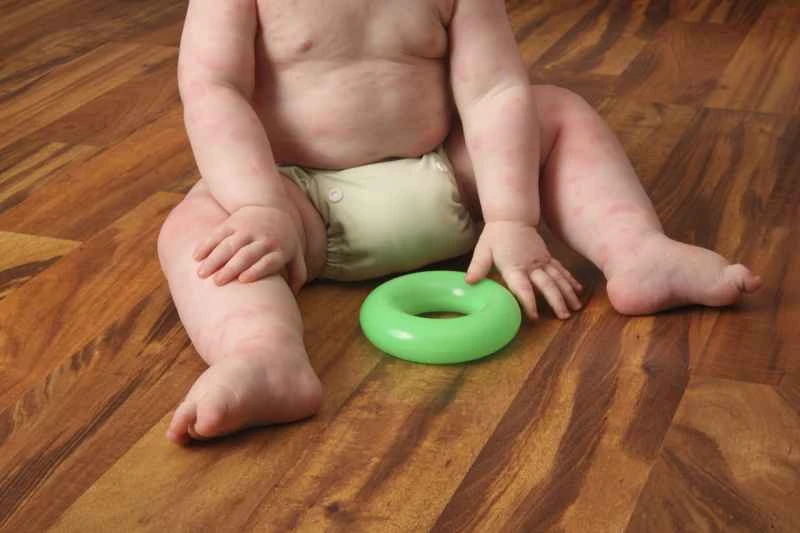

1. Mild symptoms: If the rash is small and the itching is not severe, oral second-generation antihistamines such as cetirizine or loratadine can be considered. These drugs help relieve itching, reduce wheals, and have fewer side effects such as drowsiness.
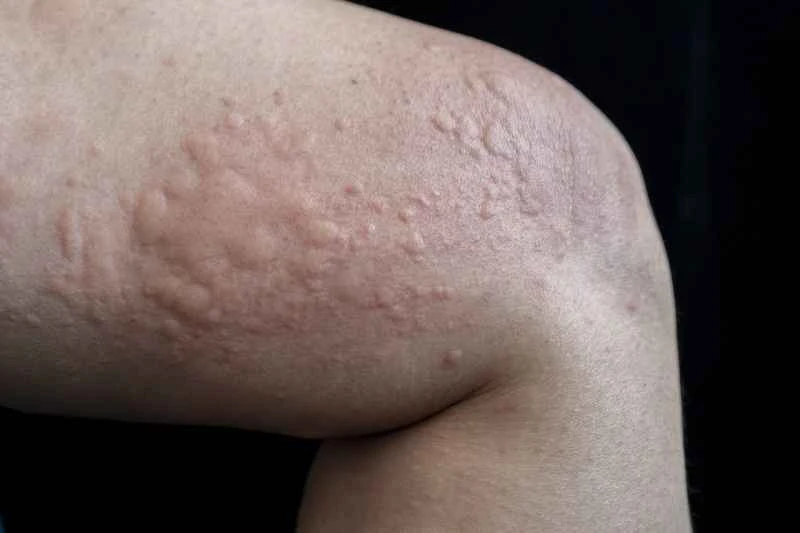
2. Recurring or severe symptoms: If the rash recurs frequently or covers a large area, the doctor may adjust the antihistamine dosage or use other medications for short-term control. Do not use steroid medications long-term without medical advice.
3. Special circumstances: If accompanied by severe conditions such as difficulty breathing or abdominal pain, immediate medical attention is required, which may necessitate emergency treatment and the use of other prescription medications.
In short, medication for urticaria needs to be tailored to the individual, and the key is to determine the treatment plan through a doctor's evaluation. Daily attention should be paid to recording triggering factors (such as food and environment), avoiding scratching the skin, and combining this with medication can better control symptoms.