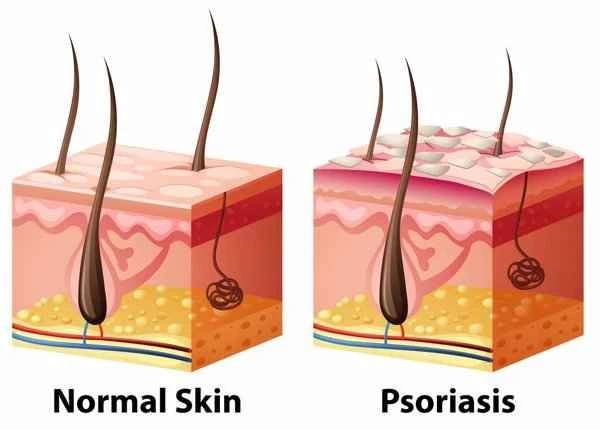
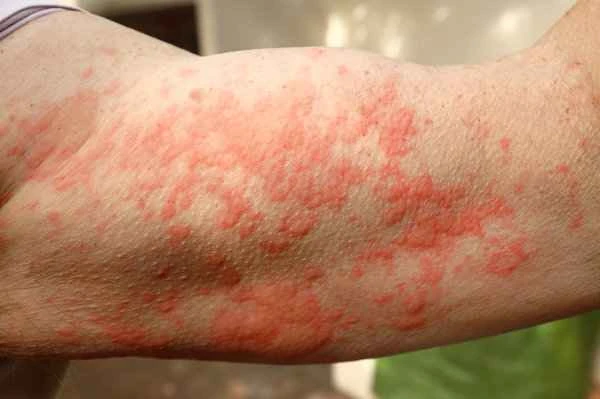
The choice of medication for treating urticaria depends on the specific condition. Doctors usually recommend appropriate medication based on the type and severity of symptoms; therefore, there is no single "best" medication. However, commonly used and effective methods include the use of antihistamines. Below are some common situations for medication selection reference:

1. **Mild Acute Onset:** If the rash is small and itching is not severe, second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine, can be tried first. These drugs usually have fewer side effects and help relieve itching and wheals.
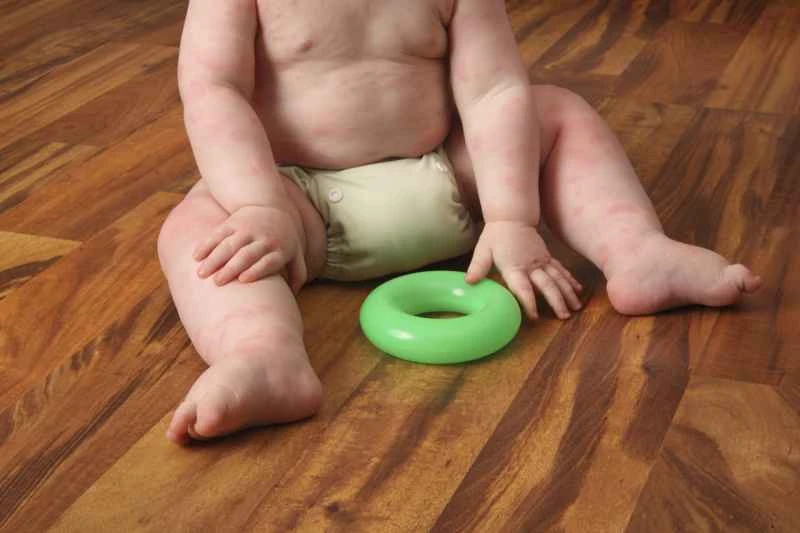

2. **Recurring or chronic symptoms**: For recurring or persistent symptoms lasting for several weeks, doctors may recommend long-term, regular use of antihistamines, adjusting the dosage or type based on effectiveness, and sometimes using different medications in combination to enhance control.
3. **Severe symptoms or swelling:** If you experience difficulty breathing, noticeable swelling of the eyelids or lips, seek immediate medical attention. Your doctor may prescribe steroids or other prescription medications for short-term relief, but these medications must be used strictly under their guidance.
It's important to note that some patients may not respond well to certain medications or may have other health problems, so self-medication carries risks. It is recommended to record the characteristics of your symptoms during an attack and provide your doctor with a detailed medical history during your consultation so that a personalized treatment plan can be developed. At the same time, avoiding known allergens, keeping your skin moisturized, and reducing scratching can also help support treatment and prevent recurrence.