Eczema tends to itch more at night, primarily due to the combined effects of physiological changes in the skin and environmental factors. Eczema is a common inflammatory skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and scaling. At night, body temperature drops, and blood circulation in the skin slows, weakening the skin barrier and making it more susceptible to external stimuli. Simultaneously, adrenaline levels decrease at night, making the skin more sensitive to itching. Furthermore, people typically reduce activity at night, lying in bed, which decreases skin friction and irritation, thus amplifying the itching sensation.
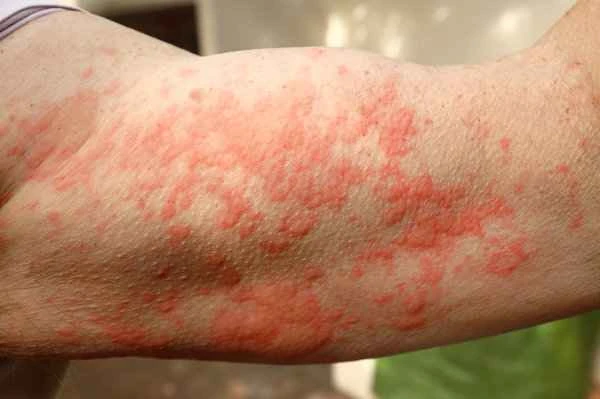
The treatment and management of eczema requires consideration of multiple factors. Using anti-inflammatory medications and moisturizers can effectively relieve symptoms and reduce skin inflammation and dryness. Maintaining good lifestyle habits, such as avoiding allergens, ensuring good indoor air circulation and appropriate humidity, can reduce eczema flare-ups. Finally, keeping the skin clean and moisturized, and avoiding the use of irritating bath products, can effectively alleviate eczema symptoms. It is important to note that eczema treatment is a long-term process that requires the joint efforts of patients and doctors, regular evaluation of treatment effectiveness, and timely adjustments to the treatment plan.
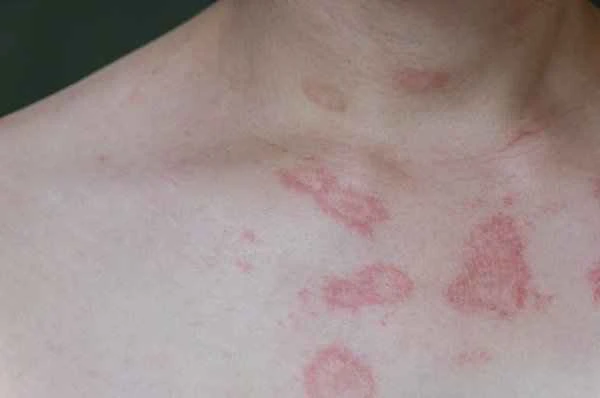
During the treatment of eczema, patients may encounter some misconceptions and challenges. For example, some patients may mistakenly believe that eczema is caused by dry skin, thus focusing only on moisturizing while neglecting anti-inflammatory treatment. Eczema treatment requires long-term adherence; some patients may stop treatment due to temporary symptom relief, leading to recurring symptoms. In the process of treating eczema, patients need to fully understand the characteristics of the disease and treatment principles, follow their doctor's guidance, and maintain good lifestyle habits to achieve the best treatment results.

[Management Tip:]
1. Use anti-inflammatory medications and moisturizers to relieve symptoms.
2. Maintain good lifestyle habits and avoid contact with allergens.
3. Regularly assess the treatment effect and adjust the treatment plan in a timely manner.