It is not contagious. Allergic urticaria is a skin condition caused by an allergic reaction to specific substances. It is not contagious, so there is no need to worry about transmitting it to others through contact or shared living. Patients are advised to identify the allergen promptly and follow their doctor's treatment plan, while also paying attention to daily skin care.
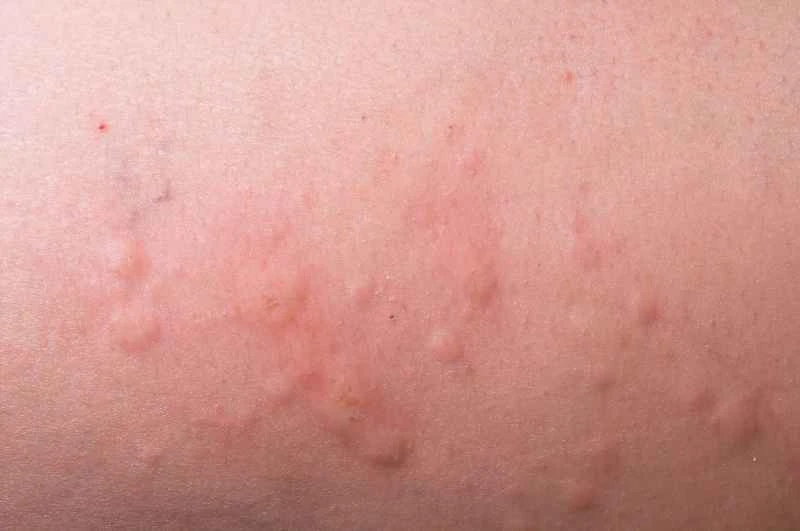
Specifically, this can be understood from the following aspects:
1. **The cause is not related to infection:** Urticaria is mainly caused by an overreaction of the human immune system to substances such as food, drugs, and pollen. It is an internal immune response and is completely different from infectious diseases caused by pathogens such as viruses and bacteria.
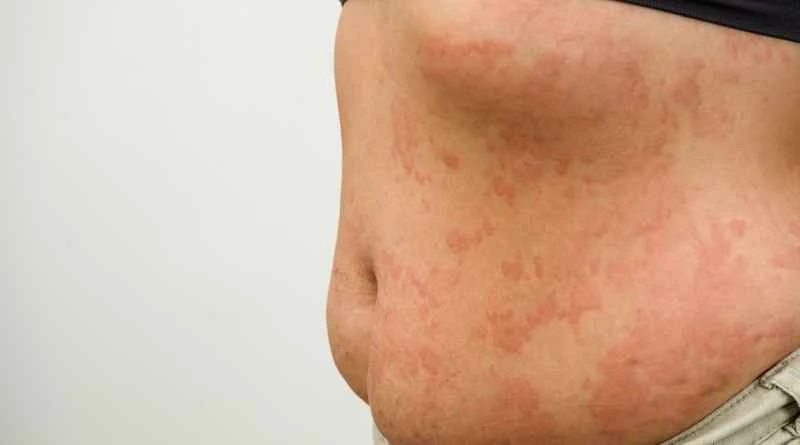
2. **Symptoms do not indicate contagiousness:** The wheals, redness, and itching on the skin are the result of local vasodilation and tissue fluid exudation. These phenomena will not be transmitted to others through the air, touch, or everyday items.
3. **Genetic factors do not affect infectivity:** Some people may be more prone to allergies due to their genetic predisposition, but this difference in constitution does not cause direct transmission between people.
If you or a family member develops hives, keep a record of changes in diet and environment before the onset of the condition to help identify the allergen; wear loose-fitting cotton clothing and avoid scratching and washing with hot water; if symptoms recur or worsen, consult a doctor promptly and use appropriate anti-allergy medication to relieve discomfort. Maintaining good lifestyle habits can help reduce the frequency of flare-ups.


