There is currently no medication that can guarantee a complete cure for urticaria, but symptoms can be effectively controlled and recurrence reduced through proper treatment and daily management. It is recommended to use medication under the guidance of a doctor and to coordinate with lifestyle adjustments.
1. Commonly used treatment drugs
Doctors often prescribe antihistamines, such as loratadine and cetirizine, to relieve itching and hives. If symptoms are severe, short-term use of steroid medications may be necessary. These medications must be used according to the prescribed course of treatment and should not be increased or decreased on your own.
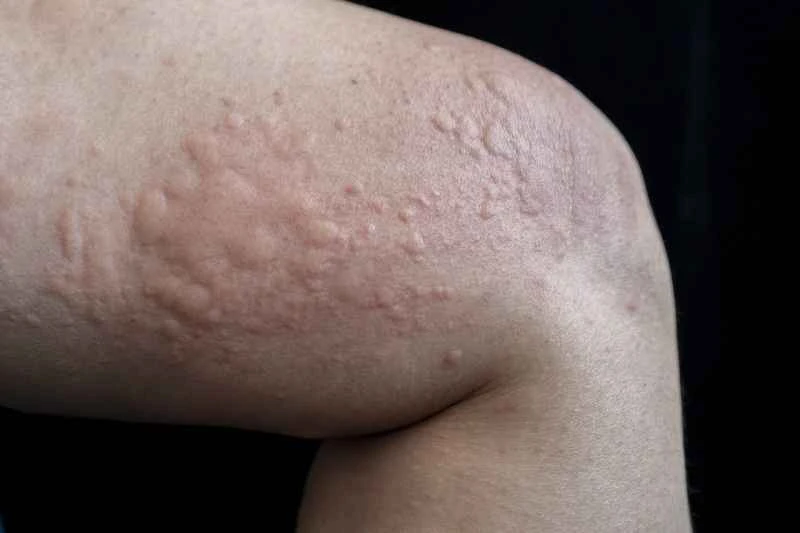
2. Targeted management of triggers
Urticaria is often triggered by allergies, infections, or physical irritants. Keeping a record of your diet and contact with substances can help identify triggers; avoid scratching your skin, wear loose-fitting cotton clothing, and minimize exposure to hot and cold stimuli.
3. Long-term conditioning approach
Some cases of chronic urticaria are related to immune system disorders. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and engaging in moderate exercise can help regulate the immune system. If flare-ups are recurrent, consult a doctor to see if allergen testing or adjustments to the treatment plan are necessary.
Pay close attention to changes in symptoms daily. If serious conditions such as difficulty breathing occur, seek medical attention immediately. Treatment requires patience; by combining medication with lifestyle management, most people can achieve long-term symptom relief.