Surgical scars can be removed or reduced through a variety of methods. Post-operative scars are part of the body's wound healing process, and the process of removing or reducing scars typically involves multiple treatment methods, including medication, physical therapy, and surgical intervention.
The key to removing or reducing postoperative scars lies in promoting healthy skin healing, reducing inflammation, and promoting normal collagen arrangement. Medication is a common approach, such as topical silicone sheets, vitamin E oil, or ointments containing corticosteroids. These medications can reduce redness and swelling, and promote softening and flattening of the scar. Physical therapies such as pressure therapy and laser therapy can also help reduce the appearance of scars. Pressure therapy reduces scar hyperplasia by applying continuous pressure, while laser therapy promotes the breakdown and remodeling of scar tissue. Finally, for severe scars, such as keloids or hypertrophic scars, surgical excision of the scar tissue may be necessary, followed by skin grafting or flap transfer techniques to repair the damaged area, thereby achieving scar reduction.
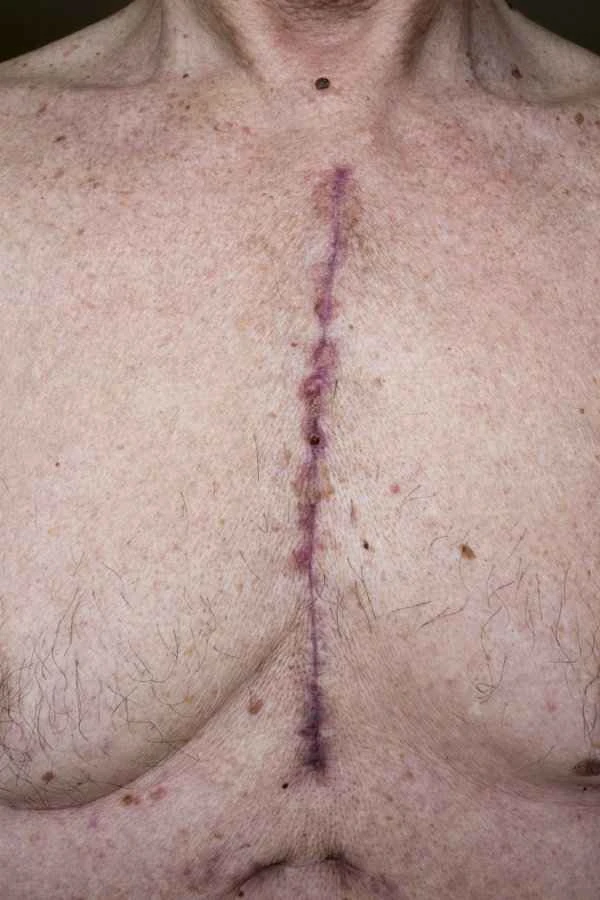
In managing postoperative scars, it's important to recognize that scar formation is a complex biological process, and different individuals and surgical sites may react differently. When choosing a treatment method, the type, size, and location of the scar, as well as the patient's overall health, must be considered. Scar treatment can be lengthy, and results vary from person to person; therefore, patients need patience and should follow their doctor's instructions.
[Management Tip:]
1. Use anti-scarring medications regularly after surgery, such as silicone sheets or vitamin E oil.
2. Follow your doctor's advice and undergo laser or stress therapy as appropriate.
3. For severe scars, such as keloids, surgical excision combined with skin grafting or flap transfer techniques should be considered.