Papular urticaria is not contagious from person to person, so parents do not need to worry about their children infecting others. It is a skin reaction caused by insect bites or contact with allergens; it is recommended to seek medical attention promptly and take daily precautions.
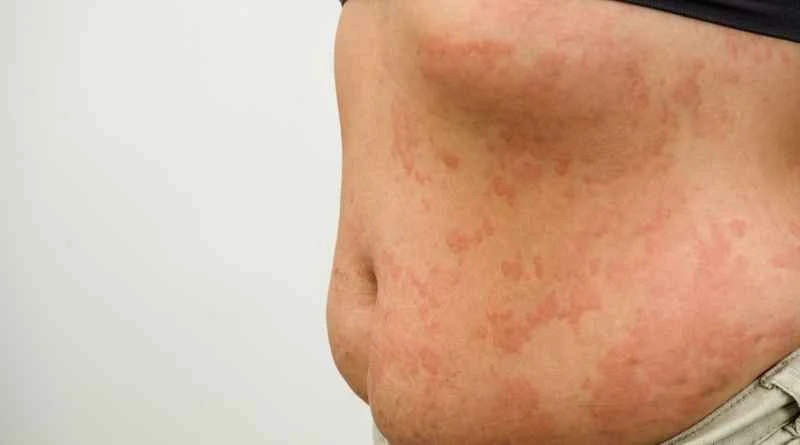
1. Causes and Contagiousness: This disease is mainly caused by an allergic reaction of the skin to the secretions of mosquitoes, mites, etc., after being bitten. Since it is a localized inflammation caused by individual constitution, it is not contagious and will not be transmitted to others through contact or respiration.

2. Typical symptoms: Red papules appear on the skin, often accompanied by significant itching, and are most commonly found on exposed areas such as the limbs and waist. The rash may recur, but usually does not spread to other parts of the body.
3. Nursing Precautions: Prevent children from scratching the rash to avoid secondary infection. Keep the home environment clean to reduce mosquito breeding; when going out, wear long-sleeved clothing and use mosquito repellent products suitable for children.
If a child's symptoms persist or worsen, consult a doctor promptly and use anti-itch or anti-allergy medications as directed. At the same time, carefully observe for and try to avoid potential allergens, such as certain plants or pet dander, to reduce the risk of recurrence.