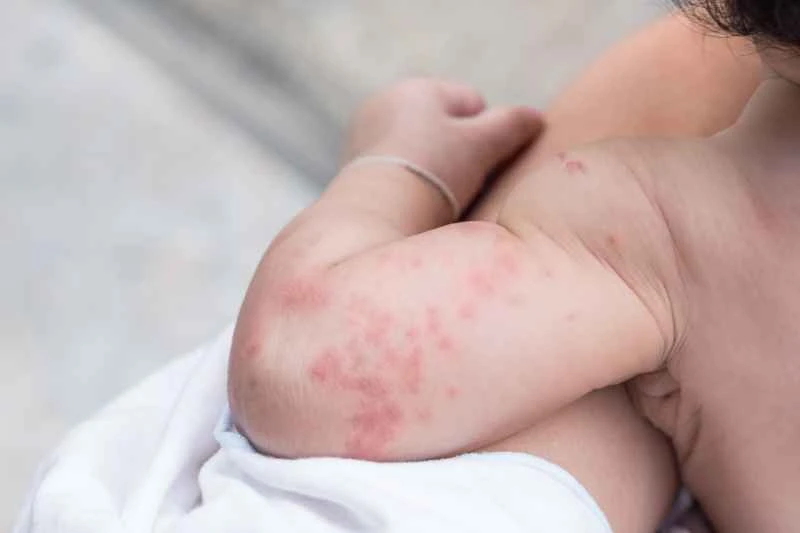
Acute urticaria is a common allergic skin reaction, usually triggered by a variety of factors, and manifests as sudden appearance of red, swollen, and itchy wheals on the skin. If symptoms occur, it is recommended to promptly identify the cause and consult a doctor.
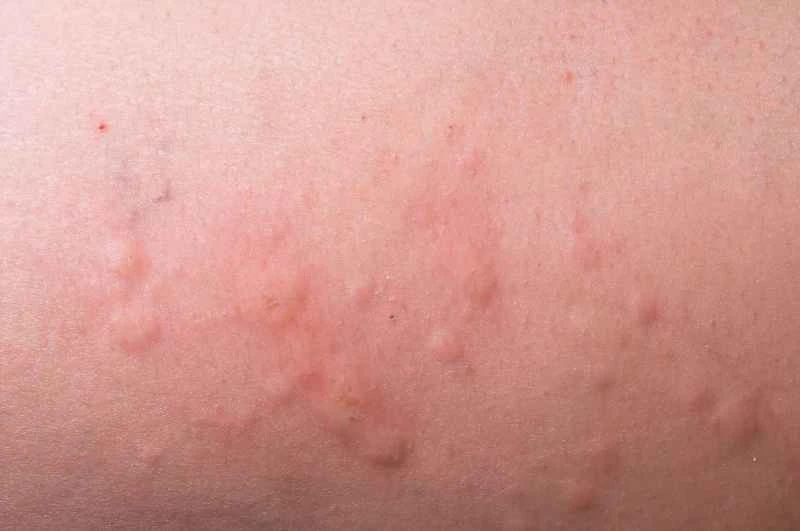
1. Common triggers: Foods such as seafood and nuts, medications such as certain antibiotics, and environmental factors such as pollen and dust mites can all trigger an attack. Infections, emotional fluctuations, or physical stimuli such as friction and stress can also cause an attack.
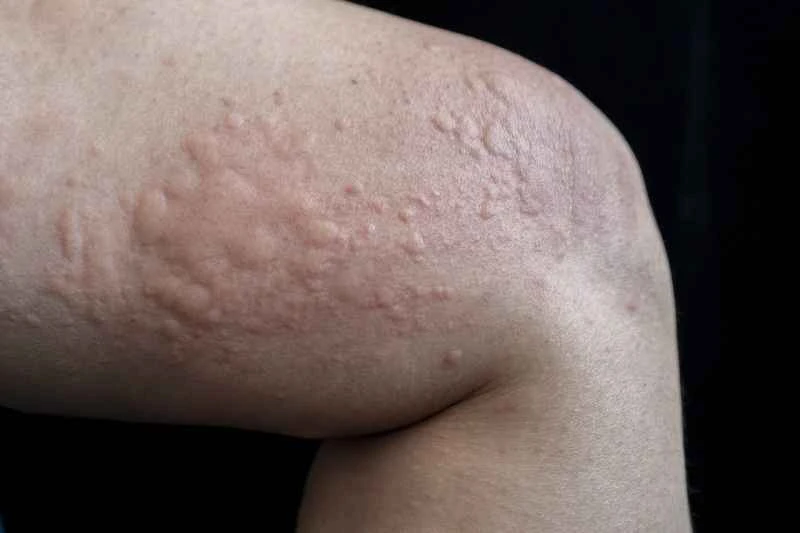
2. Symptom characteristics: Red or skin-colored wheals of varying sizes will appear rapidly on the skin, accompanied by significant itching, but they usually subside on their own within a few hours to a day, although they may recur.
3. Difference from chronic: Acute urticaria generally lasts no more than six weeks. If it recurs repeatedly for longer than this period, it may become chronic and require more systematic management.
In daily life, keep a record of your diet and environmental exposure to help identify triggers; avoid scratching during an attack, use cold compresses to relieve itching, and use anti-allergy medication as directed by your doctor. If accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.