Generalized shingles is more severe than ordinary shingles.
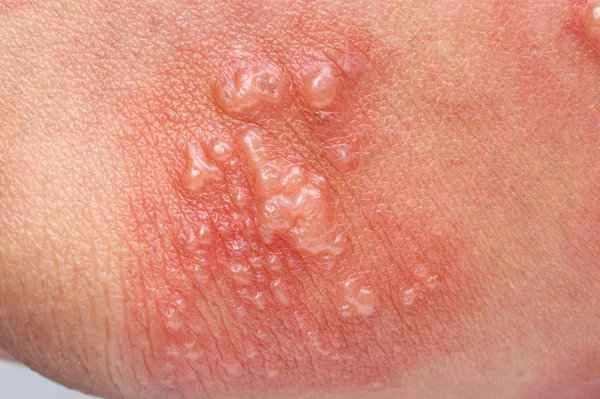
Generalized shingles is a disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. If a patient has a weakened immune system or other underlying medical conditions, the virus may multiply rapidly in the body, leading to systemic symptoms such as fever and fatigue. In addition, skin erythema and papules may appear, and some patients may experience itching. If left untreated, the skin lesions may worsen, potentially leading to bacterial infection and making treatment more difficult. Therefore, generalized shingles requires aggressive antiviral treatment, along with adequate rest, maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, and avoiding overexertion to prevent hindering recovery.
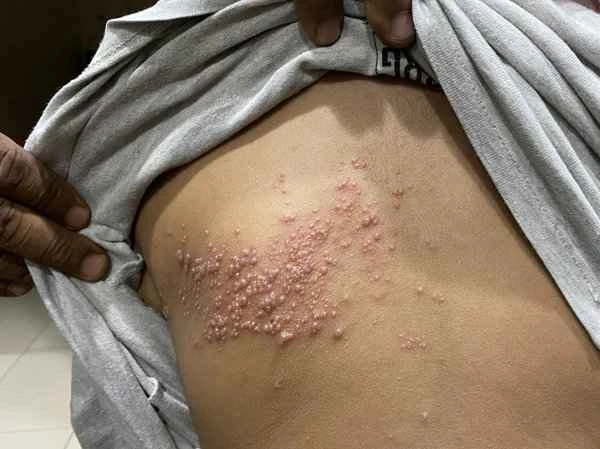
Typically, symptoms of generalized shingles may include pain, burning sensation, redness and swelling of the skin or the formation of blisters, and the pain may be more severe than that of ordinary shingles.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it is recommended that you seek medical attention as soon as possible to obtain appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
People with generalized shingles should avoid scratching the affected area to prevent secondary infection. In daily life, they should pay attention to personal hygiene, change clothes frequently, bathe regularly, and keep their skin clean and dry.