For rapid resolution of urticaria, antihistamines such as cetirizine or loratadine, commonly taken orally, can be considered under the guidance of a doctor. The following are specific precautions:
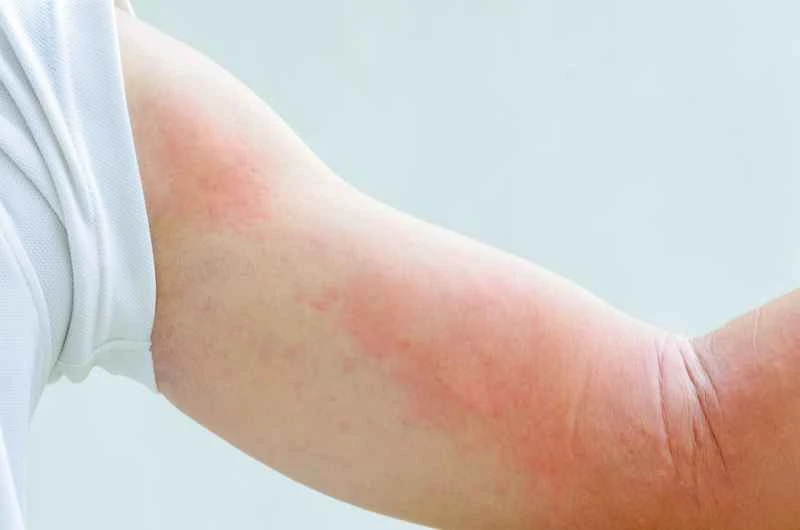
1. Seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause.
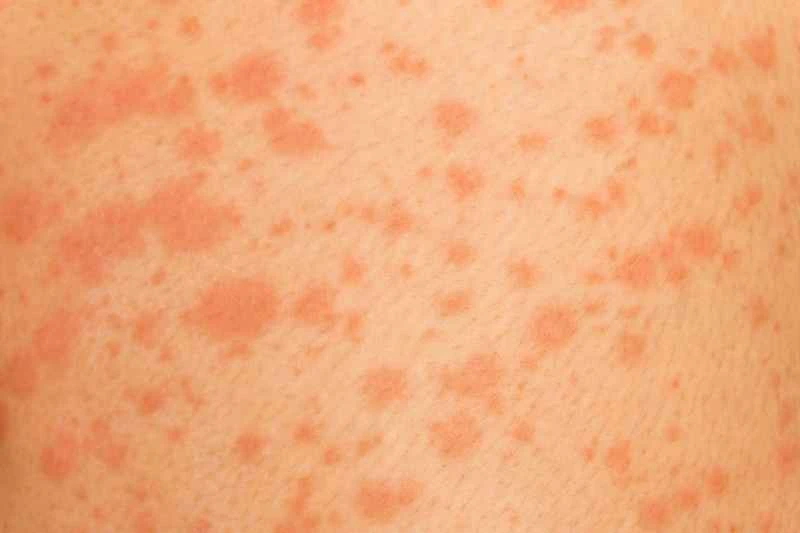
Urticaria can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies and infections. Self-medication may mask the underlying cause. It is recommended to consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and avoid misuse of medications.
2. Use antihistamines correctly.
These medications can relieve itching and hives, but should be taken as directed in the package insert or as prescribed by a doctor. Some medications may cause drowsiness; therefore, driving or working at heights should be avoided while taking these medications.
3. Combine with daily care to accelerate recovery
Applying cold compresses to the affected area can relieve itching while taking medication, and wearing loose cotton clothing can reduce friction. Keeping a record of changes in diet and environment can help identify and avoid triggering factors.
If symptoms do not improve after medication or if you experience shortness of breath, swelling of the eyelids or lips, please seek medical attention immediately. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and engaging in moderate exercise can help reduce the risk of recurrent urticaria.


