For hives, it is recommended to first consult a dermatologist. This is a common skin problem, and dermatologists can provide professional diagnosis and standard treatment plans. If the condition is complex or recurrent, assistance from other departments may be necessary.
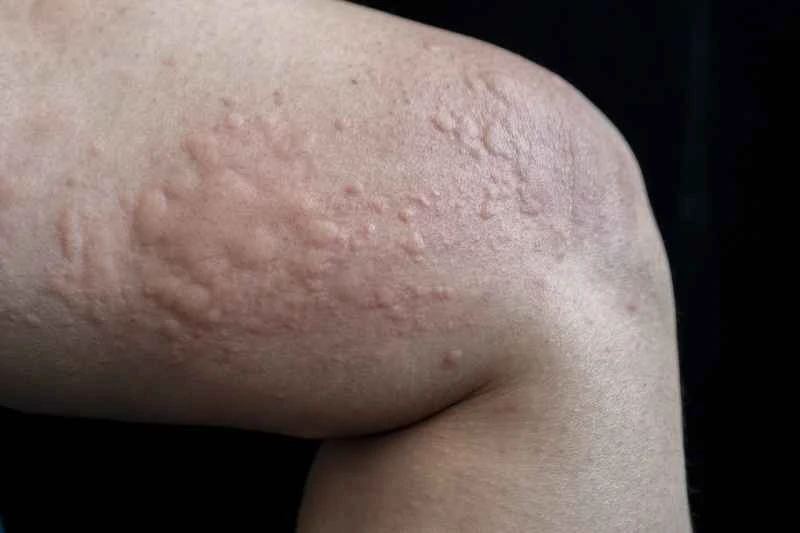
For specific medical treatment options, please refer to the following points:
1. Dermatology is the first choice: The vast majority of urticaria cases are treated by a dermatologist. The doctor will examine the rash, inquire about the triggers, and often use antihistamines to control itching and wheals.
2. When accompanied by other symptoms: If urticaria is accompanied by significant palpitations, difficulty breathing, abdominal pain or joint swelling, it may be necessary to see an emergency room doctor or consult an allergist or rheumatologist based on the symptoms to rule out other systemic factors.
3. Recurrent or unexplained: If the rash recurs and conventional treatments are ineffective, you can go to the allergy department for more detailed allergen testing, or have a doctor assess whether you need to be referred to a relevant internal medicine department.
It is recommended that you choose the dermatology department for your first visit. Before your appointment, you can briefly record the time, appearance, and possible triggers (such as food, medication, contact agents) of the rash, as well as any medications you have taken. This will help the doctor make a faster diagnosis. In daily life, avoid known triggers and use medications as prescribed by your doctor; do not use medications for extended periods without medical advice.