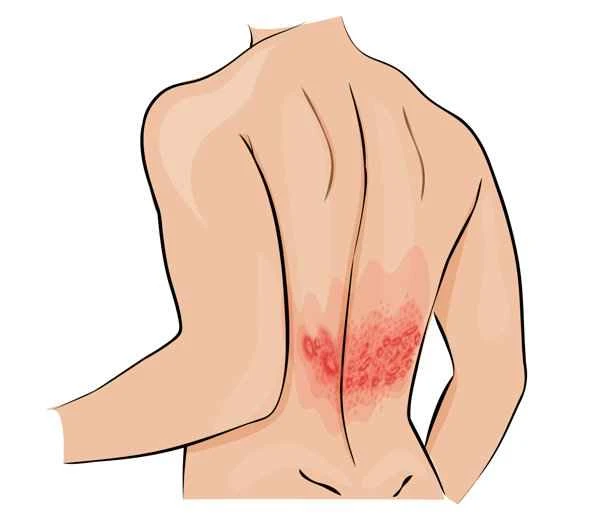
Keloid-prone individuals are those whose bodies are prone to developing excessive scar tissue during wound healing. Medication control involves intervening with drugs to reduce scar formation or improve existing scars. The medication control for keloid-prone individuals primarily relies on the mechanisms of action of the drugs, which typically work by inhibiting fibroblast proliferation, reducing collagen synthesis, and promoting scar softening.
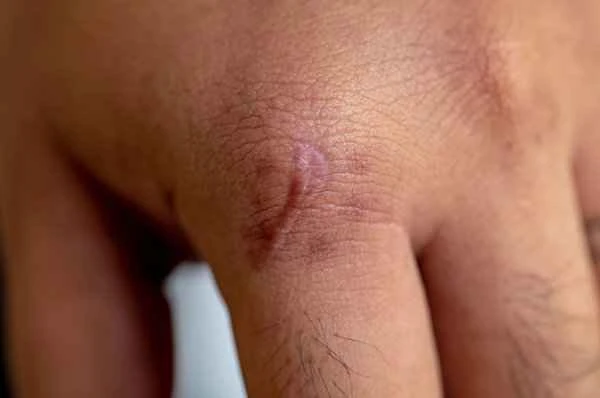
In terms of medication control, commonly used drugs include glucocorticoids, vitamin E, and silicone gel. Glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, can reduce scar formation by inhibiting inflammatory responses and fibroblast proliferation. Vitamin E helps promote skin cell regeneration, reducing scar formation. Silicone gel reduces scar formation by forming a protective film and helps soften and flatten existing scars. These drugs can work synergistically to control scarring. For example, vitamin E can promote skin cell regeneration, while glucocorticoids can inhibit inflammatory responses; the combination of the two can more effectively control scar formation.
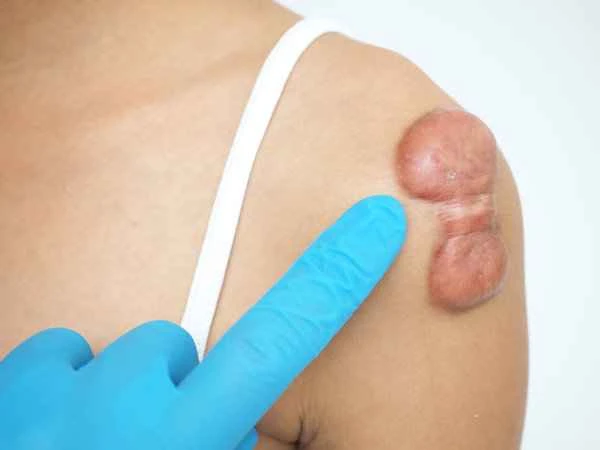
During medication management, it's important to note that while drugs can play a role in controlling keloid scarring, they are not suitable for all patients. The potential side effects and risks of medication must be fully considered. For example, long-term use of glucocorticoids may lead to a range of side effects, such as osteoporosis and hypertension. When choosing medication, individual patient differences, drug side effects, and long-term treatment outcomes must be comprehensively considered. Furthermore, medication should be administered under the guidance of a professional physician to ensure safety and effectiveness.
[Management Tip:]
1. A comprehensive skin examination should be performed before using any medication to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
2. Monitor for drug side effects regularly, and seek medical attention promptly if any abnormalities occur.
3. Avoid purchasing and using medications on your own; use them under the guidance of a doctor.
4. Maintain good lifestyle habits, such as avoiding excessive sun exposure and keeping your skin clean.