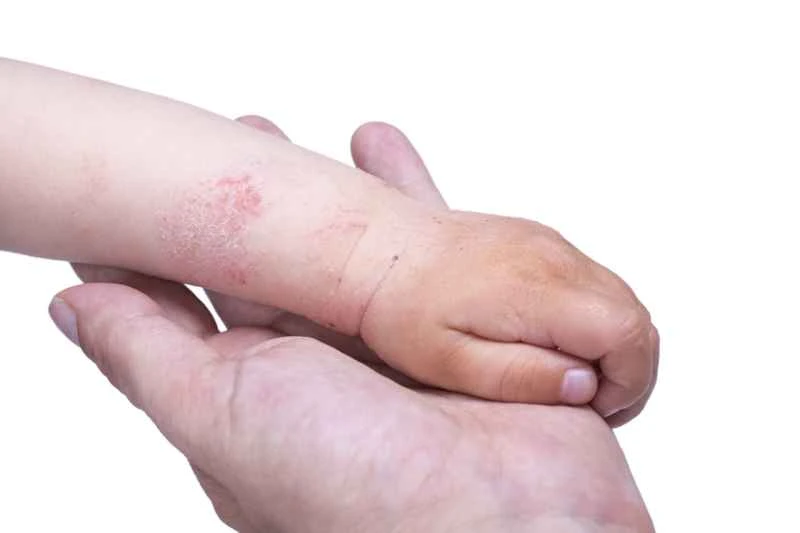
Psoriasis is not caused by contagious or infectious agents, but is a chronic skin condition related to internal factors. It is primarily associated with immune system dysfunction, genetic predisposition, and environmental factors, so there is no need to worry about it being transmitted to others through daily contact. Patients are advised to maintain healthy lifestyle habits and seek professional medical guidance.
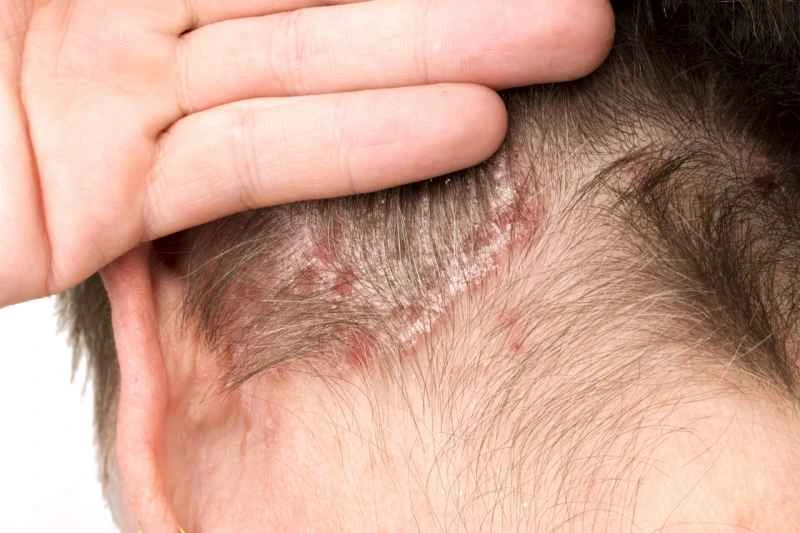
Specifically, the occurrence of psoriasis usually involves the following aspects:
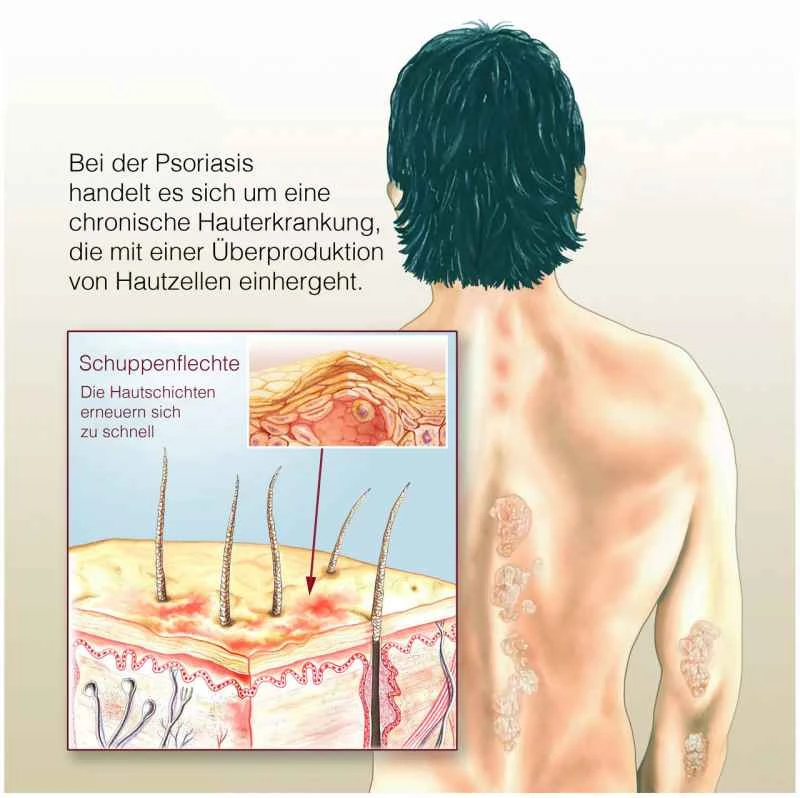
1. Genetic factors: Some patients have a family history of the disease. If parents have psoriasis, their children are more likely to develop the disease, but this does not mean that they will definitely develop the disease.
2. Immune system effects: An overactive immune system may lead to accelerated skin cell growth, resulting in common erythema and silvery-white scales.
3. Environment and lifestyle: Factors such as mental stress, skin damage, infection or climate change may induce or aggravate symptoms, and habits such as smoking and drinking may also have an impact.
While psoriasis is currently difficult to cure completely, it can be effectively controlled through proper treatment. It is recommended to avoid scratching the skin, use gentle moisturizing products, reduce stress, maintain a regular sleep schedule, and consult a dermatologist promptly to develop a long-term management plan tailored to your individual situation to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.