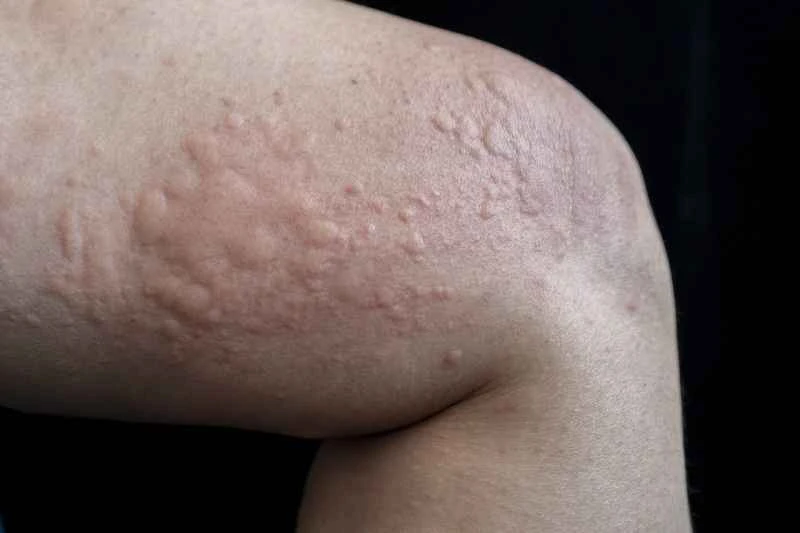
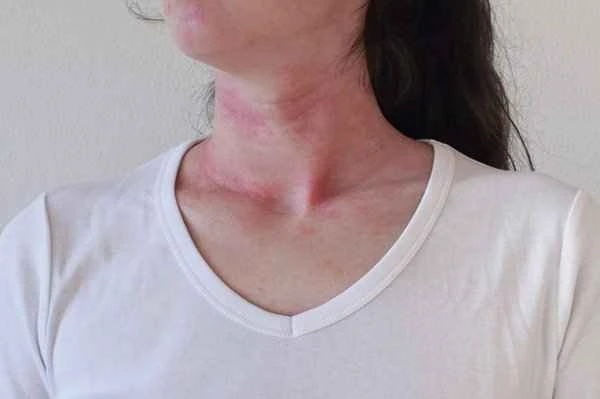
Shingles is a skin infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Once diagnosed, prompt treatment is necessary. The primary task in dealing with shingles is to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Medication can alleviate symptoms, shorten the course of the disease, and prevent complications. Antiviral drugs are key to treating shingles; they inhibit viral replication and reduce viral spread, thereby reducing pain and the severity of the rash. Pain relievers and topical treatments are also important components of treatment; they can relieve pain and promote skin healing. During treatment, patients also need to rest, maintain good nutrition, and avoid stress, all of which help accelerate the recovery process.
There are some potential risks and common misconceptions to be aware of during the treatment of shingles. Antiviral medications should be started within 72 hours of the onset of symptoms for optimal effectiveness. Some patients may mistakenly believe that shingles is a common skin problem, thus delaying optimal treatment. In fact, if shingles is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications such as neuralgia, affecting the patient's quality of life. Once shingles symptoms appear, seek professional medical help immediately and avoid self-medication or ignoring the condition.
[Management Tip:]
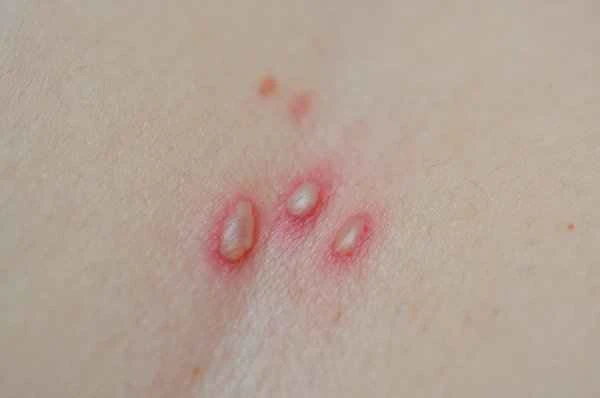
1. Seek medical attention as soon as possible and accept the diagnosis and treatment advice of a professional doctor.
2. Take antiviral medication as prescribed by your doctor, and pay attention to pain relief and local treatment.
3. Maintain good rest and nutrition, and avoid overwork and mental stress.