Hives in children are not contagious, so you can rest assured. This is a common allergic skin reaction, usually caused by food, medication, infection, or environmental factors. Parents are advised to carefully observe the items their child comes into contact with daily and keep a record of any flare-ups for reference when seeking medical attention.
This can be understood from the following aspects:
1. **The difference between etiology and transmission**
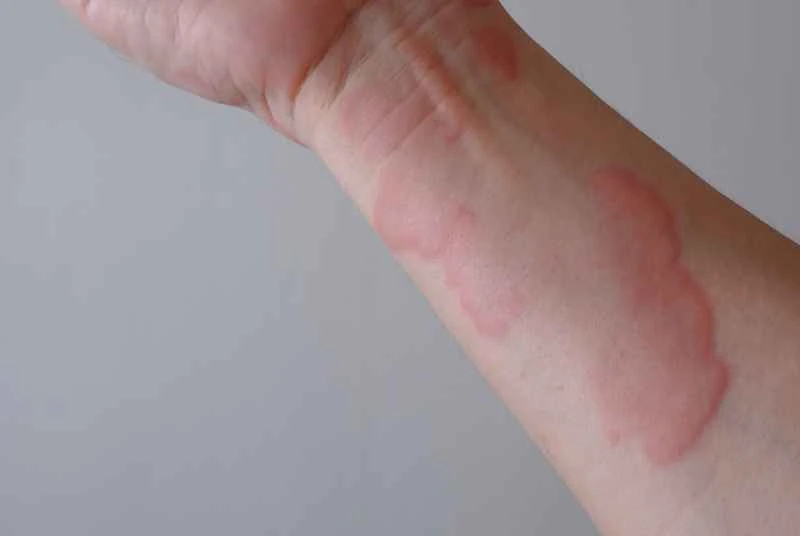
Urticaria (hives) is an allergic reaction of the body's immune system to certain substances, such as seafood, pollen, or insect bites. Unlike colds or chickenpox, it is not transmitted through viruses or bacteria and therefore is not contagious from person to person.
2. **Common Symptom Manifestations**
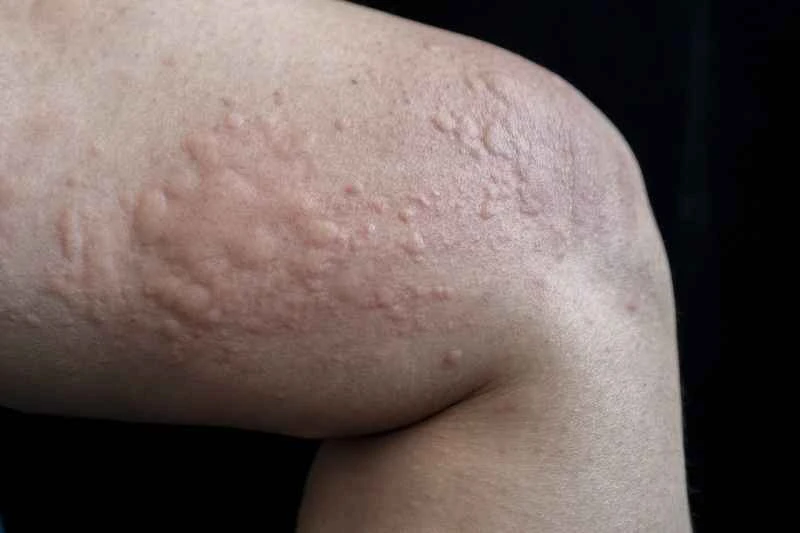
The child may develop red or skin-colored wheals accompanied by itching, but the rash usually subsides within a few hours and may recur. Although these symptoms may seem obvious, they are only related to the child's own constitution and will not affect those around them.
3. **Precautions for Home Care**
Although not contagious, parents should take precautions to prevent children from scratching their skin to avoid secondary infections. Dress children in loose-fitting cotton clothing and use a doctor-recommended anti-itch cream. Also, noting and recording factors that may trigger the rash can help prevent recurrence.
If a child experiences recurrent hives, it is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to identify the allergen and adjust their diet or living environment under the guidance of a doctor. Maintaining home cleanliness and reducing contact with common allergens such as dust mites and pet dander can gradually help alleviate the child's discomfort.


