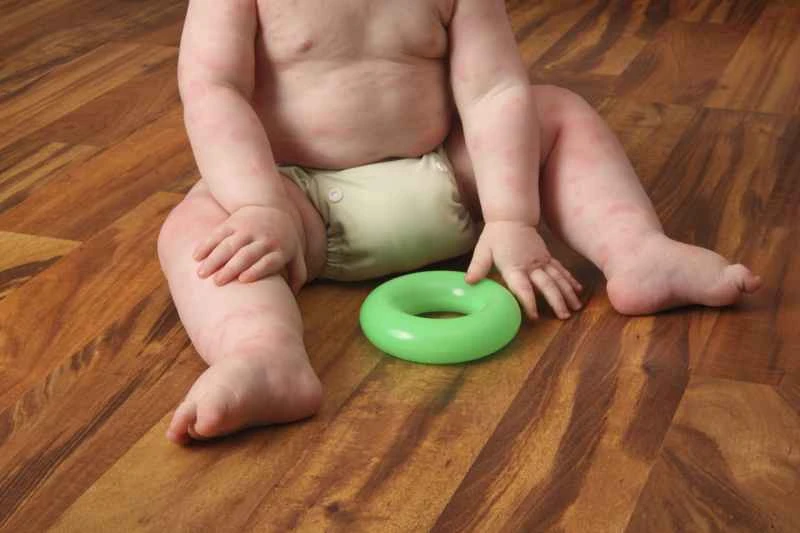
Mild urticaria usually resolves on its own. Urticaria is a common skin condition characterized by red or skin-colored patches of skin, accompanied by intense itching. Mild urticaria refers to cases with mild symptoms and no serious complications. In such cases, urticaria typically resolves on its own within days to weeks.
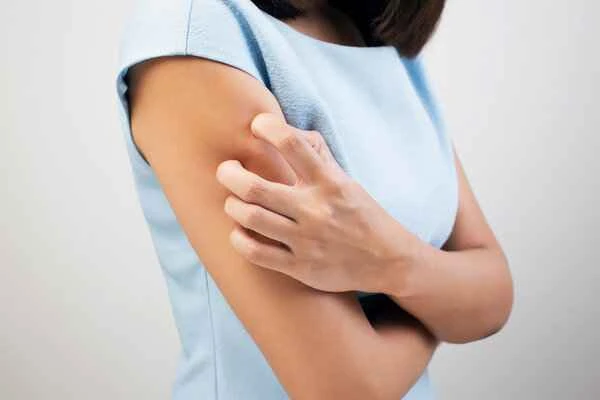

Urticaria (hives) occurs when the body reacts to certain irritants, causing blood vessels under the skin to dilate and tissue fluid to leak out, forming red patches. The self-healing mechanism of mild urticaria mainly relies on the body's own immune regulation and repair functions. As the irritant disappears or the body adapts, the immune system gradually returns to normal, ceasing the release of chemicals that trigger allergic reactions, thus gradually reducing and eventually eliminating urticaria symptoms. Patients with mild urticaria usually do not experience serious complications, and their bodies can repair damaged skin tissue on their own, further promoting symptom relief.
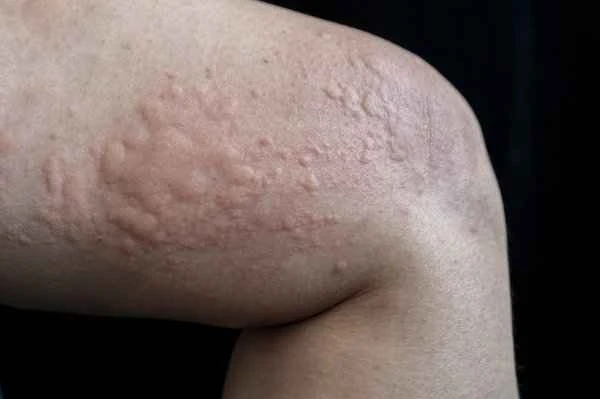
When considering whether urticaria (hives) will resolve on its own, it's important to be aware of some potential risks and misconceptions. While mild urticaria often resolves on its own, prolonged or recurring symptoms may indicate an underlying chronic condition or allergen, requiring further examination and treatment. Although mild urticaria symptoms are mild, patients should still avoid contact with known allergens to prevent worsening of symptoms. Finally, even with mild symptoms, some patients may be at risk of potential complications such as difficulty breathing; therefore, prompt medical attention is crucial if severe symptoms occur.
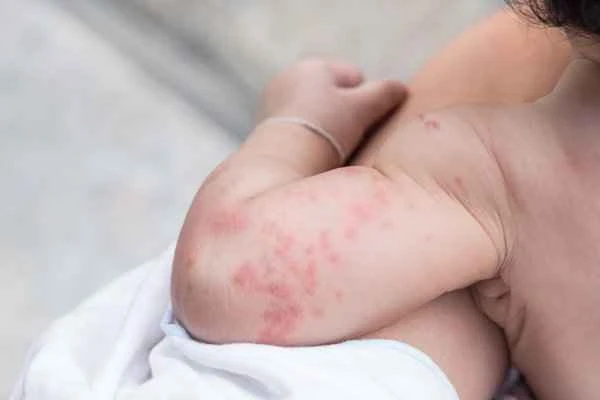
[Management Tip:]
1. Avoid known allergens, such as certain foods, medications, or environmental factors.
2. Monitor for changes in symptoms regularly. If symptoms continue to worsen or new symptoms appear, seek medical attention promptly.
3. Maintain good lifestyle habits, such as regular sleep and a healthy diet, to enhance the body's immunity.


