When choosing a medication for urticaria, it is generally recommended to use ointments containing antihistamines or weak steroids under the guidance of a doctor. However, the specific effects vary from person to person and depend on the type and severity of the rash.

1. **Common Types of Topical Medications**
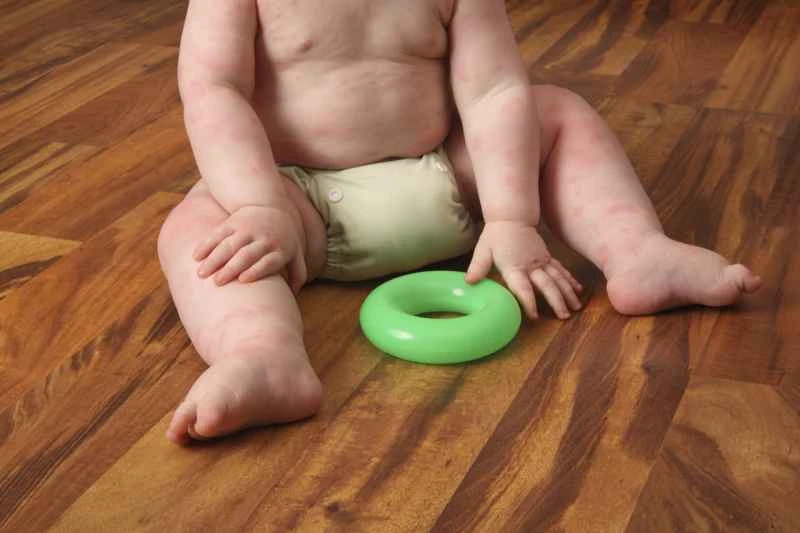

Commonly available ointments fall into two main categories: one is creams containing antihistamines (such as diphenhydramine), which can help relieve itching; the other is mild corticosteroid ointments (such as hydrocortisone), suitable for mild red and swollen rashes. Over-the-counter ointments may provide some relief for mild symptoms.
2. **Handling methods for different situations**
If the rash is small and the itching is not severe, you can try applying a cold compress or using a cooling soothing cream first. If the rash recurs, covers a large area, or is accompanied by severe swelling, the effect of using ointment alone may be limited. In this case, it is necessary to combine it with oral medication (such as antihistamines) and avoid scratching to prevent further skin irritation.
3. **Precautions and Contraindications**
Cleanse the skin before applying the ointment, avoiding broken skin. Hormonal ointments should not be used for extended periods or over large areas; use with caution on children or sensitive areas. If burning or worsening of the rash occurs after application, discontinue use immediately and consult a doctor.
In summary, the choice of urticaria ointment should be based on individual circumstances. Mild symptoms can be treated with mild topical medications, but if there are recurrent or obvious symptoms, you should seek medical attention in time to check the cause and receive comprehensive treatment under professional guidance. At the same time, pay attention to recording allergens, keeping skin moisturized and maintaining a regular schedule to reduce recurrence.