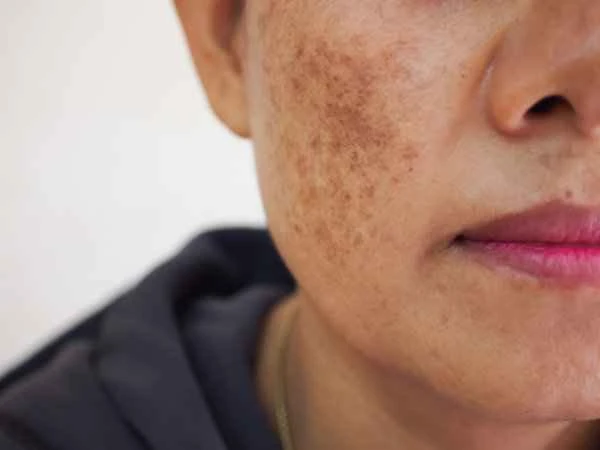
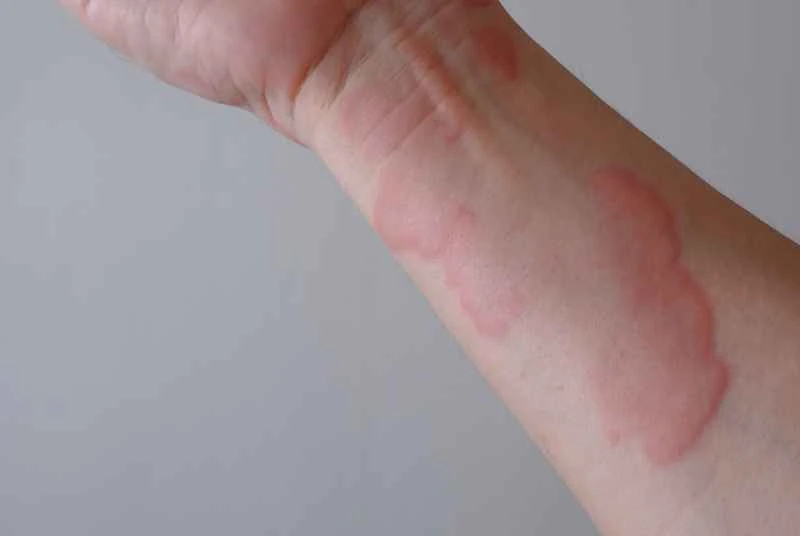
Scar inflammation refers to an inflammatory reaction in existing scar tissue, which requires timely treatment to prevent the spread of infection.
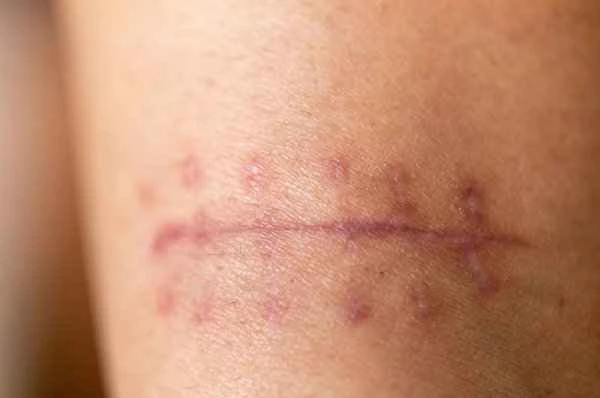
The management of scar inflammation requires a comprehensive consideration of the severity of the inflammation, the type of scar, and the patient's overall health. Keeping the wound clean is a key step in preventing the spread of infection; the wound can be cleaned with saline solution to remove surface dirt and secretions. Topical application of antibiotic ointments or anti-inflammatory drugs can effectively inhibit bacterial growth and reduce the inflammatory response. In some cases, if the scar inflammation is severe, oral or intravenous antibiotics may be necessary to control the infection. Keeping the skin around the wound moist helps accelerate the healing process; ointments or gels containing moisturizing ingredients can be used. During the management of scar inflammation, avoid squeezing or damaging the scar tissue to prevent further damage or infection.
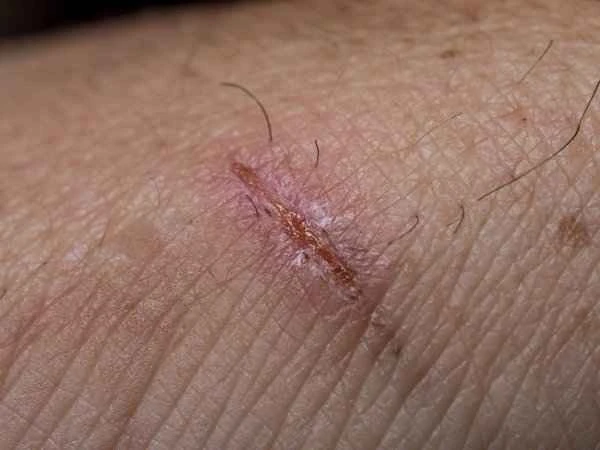
When treating scar inflammation, it's important to avoid using overly harsh cleansers, as these can worsen the inflammatory response. Additionally, scar inflammation can be a symptom of certain chronic diseases; for example, diabetic patients are more prone to wound infections. Therefore, while treating scar inflammation, it's also crucial to monitor the patient's overall health and, if necessary, undergo appropriate examinations and treatments.
[Management Tip:]
1. Keep the wound clean and avoid using overly irritating cleaning agents.
2. Apply topical antibiotic ointment or anti-inflammatory drugs to control the infection.
3. Monitor wound healing regularly and seek medical attention promptly if necessary.
4. Pay attention to the patient's overall health condition, especially for patients with chronic diseases.