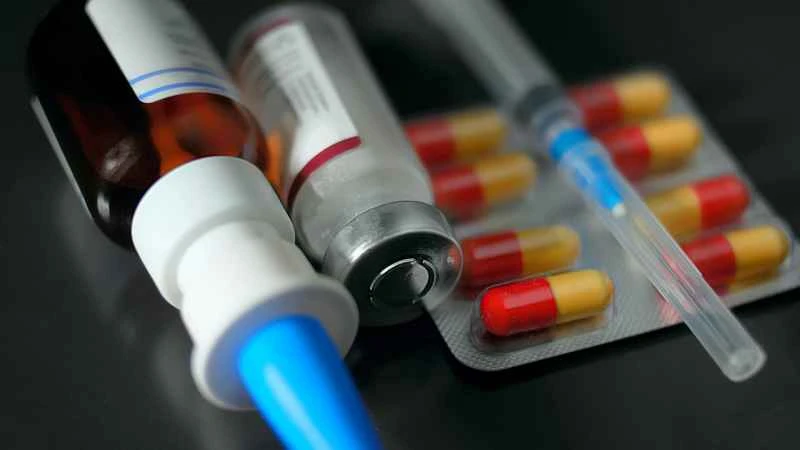
Treatment for urticaria usually requires selecting medication based on the specific situation. Commonly used medications include antihistamines, and it is recommended to use them under the guidance of a doctor. Below are some common situations requiring medication reference:
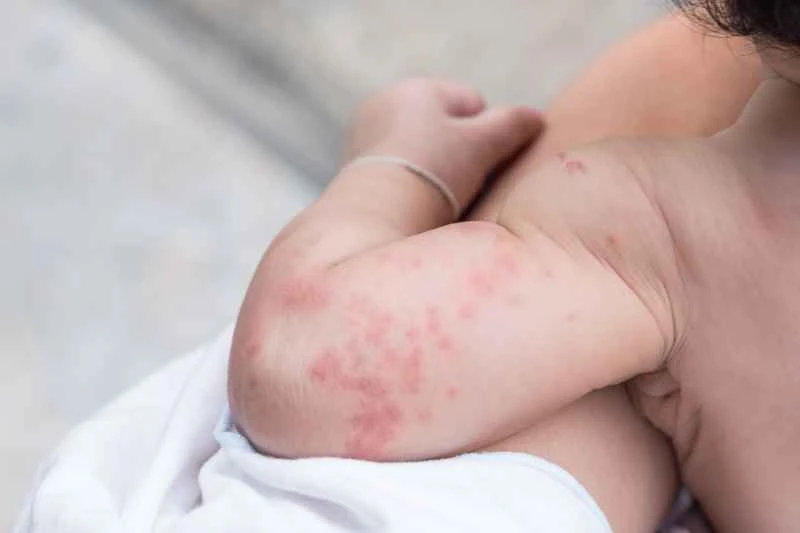
1. Mild symptoms: If the rash is minor and itching is not severe, you can try using second-generation antihistamines, such as loratadine or cetirizine. These medications are usually taken once a day and have minimal impact on daily activities.
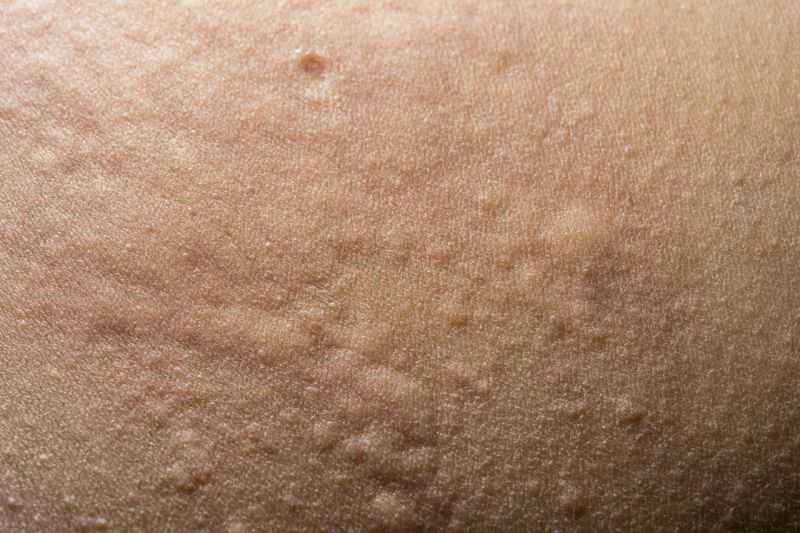
2. Recurrent attacks: For chronic urticaria that frequently recurs, doctors may recommend long-term, regular use of antihistamines to control symptoms and reduce the frequency of attacks. Do not adjust the dosage on your own.
3. Acute severe attack: If a large area of rash, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the eyelids and lips occurs, seek medical attention immediately. The doctor may use other types of medications for emergency treatment in the short term.
In daily care, try to avoid scratching your skin, wear loose cotton clothing, and reduce washing with hot water. Keeping a record of your diet and contact with substances can help identify possible triggers.
If symptoms do not improve or worsen after taking medication, please return for a follow-up appointment to adjust the treatment plan. Everyone's constitution is different, and suitable medications may vary; following your doctor's instructions will ensure safer and more effective control of the condition.