Urticaria is a common allergic skin reaction that is usually treatable but prone to recurrence. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to identify the triggers and follow the doctor's instructions for long-term management.
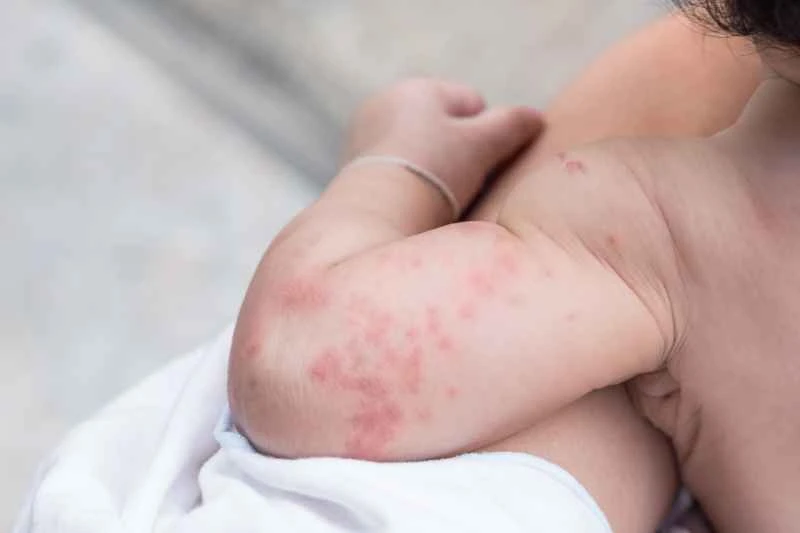
1. Disease characteristics: Red or skin-colored wheals of varying sizes appear on the skin, accompanied by significant itching. Symptoms may appear suddenly and subside within hours, but are prone to recurrence.
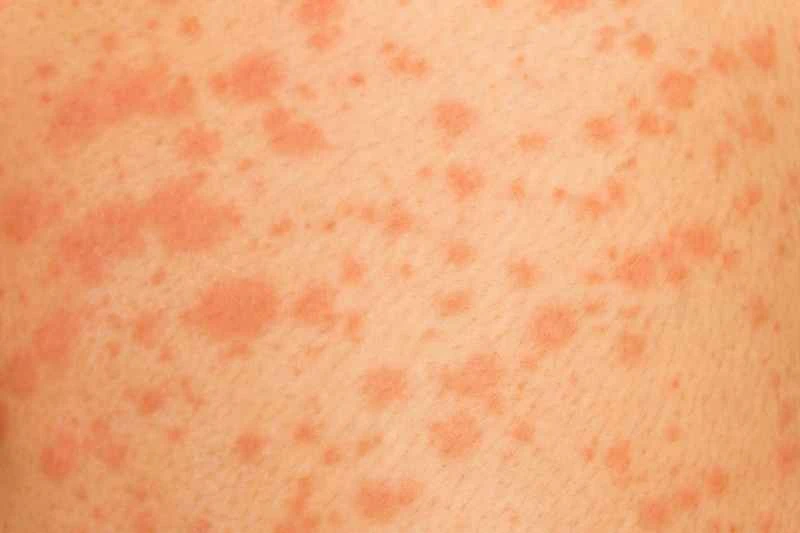
2. Treatment: Most patients can effectively control their symptoms with anti-allergy medications, but some cases of chronic urticaria require a longer period of treatment. The triggers are complex, including food, environmental changes, and stress.
3. Management points: Treatment should be combined with daily observation and recording possible triggering factors; avoid scratching the skin, and wearing loose cotton clothing can help reduce irritation.
It is recommended to start with lifestyle details: keep your living environment clean and well-ventilated, and keep a record of foods that may cause allergies; consult a doctor promptly for medication during acute flare-ups, and chronic patients can keep a symptom diary to help the doctor adjust the treatment plan. Maintaining a good sleep schedule and a stable mood also play a positive role in alleviating symptoms.