People with a tendency to form keloids are prone to developing excessive scarring after injury. However, scientific methods can be used to reduce the formation of scars.
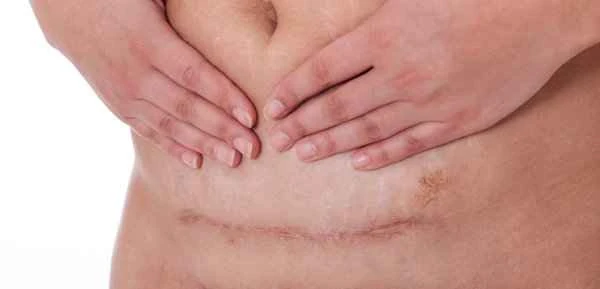
Keloid-prone skin refers to a condition where the body is prone to developing excessively proliferative scars during the wound healing process after injury. These scars not only affect appearance but can also cause discomfort such as pain and itching. The causes are mainly related to genetic factors, skin tension lines, wound location, and infection. In cases of keloid-prone skin, fibroblasts become overactive during the healing process, leading to excessive collagen synthesis and the formation of overgrown scars.
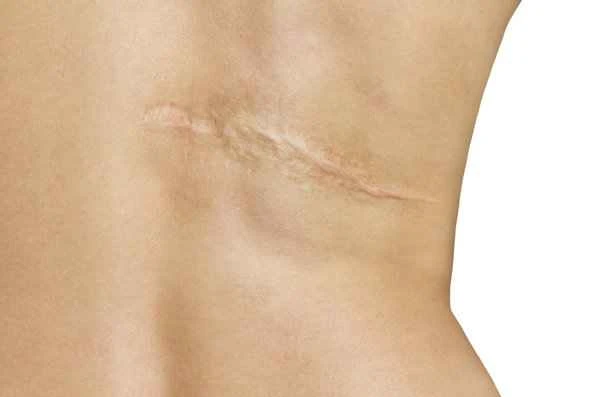
To reduce scarring, it's crucial to clean and disinfect the wound immediately after injury to prevent infection, as infection can worsen scarring. Medications can be used to promote wound healing, such as silicone sheets or scar patches. These products keep the wound moist and reduce scar formation. Topical steroid injections can also inhibit excessive scar growth. Maintaining wound moisture is essential during healing; moisturizers like petroleum jelly can help. Simultaneously, avoid pulling or rubbing the wound to reduce the likelihood of scar hyperplasia.
[Life Tips:]
1. Clean and disinfect the wound immediately after injury to prevent infection.
2. Use products such as silicone sheets or scar patches to help the wound heal.
3. Keep the wound moist and use a moisturizer to promote healing.
4. Avoid pulling and rubbing the wound to reduce scar hyperplasia.


