Keloids are overgrown scar tissues, and the key to controlling their growth lies in inhibiting abnormal fibrosis. Keloids form because after skin injury, fibroblasts become overactive, leading to excessive collagen synthesis and the formation of scar tissue that extends beyond the original wound. The core of controlling keloid growth lies in inhibiting excessive fibroblast proliferation and reducing collagen deposition.
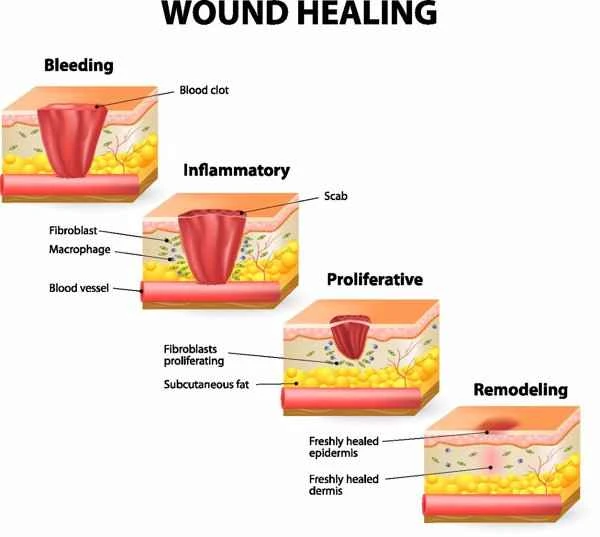
To control the growth of keloids, various treatment methods can be employed, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery. In terms of medication, corticosteroid injections are a commonly used method, reducing the size of keloids by inhibiting the inflammatory response and fibroblast proliferation. Physical therapy, such as pressure therapy, limits the growth of scar tissue by applying continuous external pressure. Surgical treatments include excision and laser therapy, which physically remove scar tissue. However, it's important to note that surgery may stimulate regrowth of scar tissue; therefore, postoperative treatment usually requires the use of other therapies to prevent keloid recurrence.
There are some common misconceptions in the treatment of keloids, such as believing that all types of scars can be controlled with the same treatment, or relying too much on a single treatment method while neglecting the importance of comprehensive treatment. In reality, keloid treatment requires a customized treatment plan based on the individual's specific situation, including factors such as the size, location, and shape of the scar, as well as the patient's overall health. Side effects may occur during treatment, such as local skin pigmentation or allergic reactions. Therefore, it is essential to fully understand the potential risks before treatment and to undergo treatment under the guidance of a doctor.
[Management Tip:]
1. Regularly monitor changes in the size and shape of keloids.
2. Avoid unnecessary stimulation or friction on keloids.
3. Seek medical attention promptly if redness, swelling, pain, or other abnormal symptoms occur.
4. Follow your doctor's advice during treatment and use a combination of treatment methods.