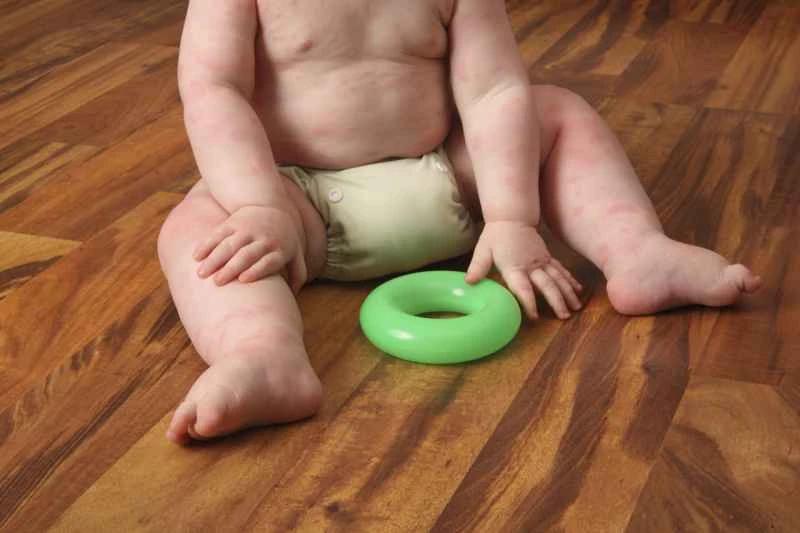
Eczema is not contagious through contact, so everyday clothes usually do not need to be washed separately. However, if the skin is broken or oozing, proper clothing care can help reduce irritation and the risk of secondary infections.
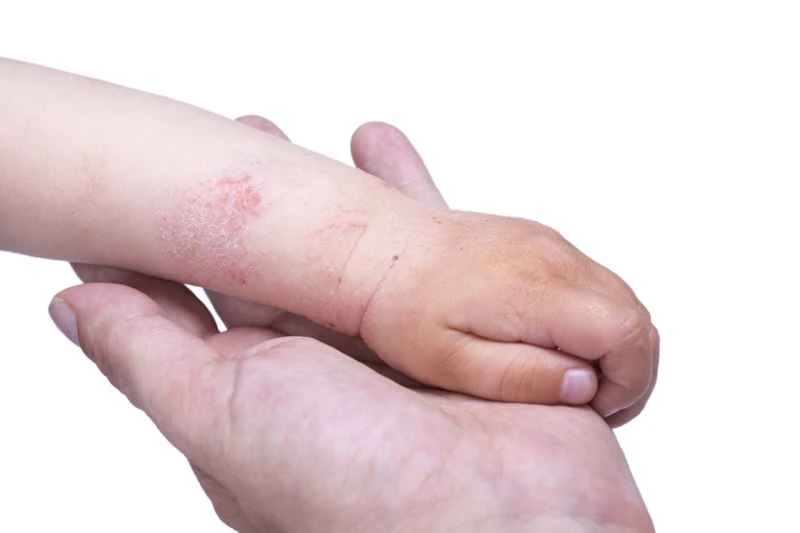
This can be understood from the following two aspects:

1. **The contagiousness of eczema**
Eczema is an autoimmune-related skin condition, not directly caused by pathogens such as fungi or bacteria. Healthy individuals who come into contact with the skin, clothing, or personal items of an infected person will generally not develop a similar rash.
2. **Clothing Disposal Suggestions**
• For daily use: Simply wash as usual, using a mild detergent and rinsing thoroughly to avoid skin irritation from residual chemicals.
• Special circumstances: If the eczema area is oozing, crusted, or infected, you can wash your underwear separately and soak it in hot water above 60°C or disinfectant to help reduce microorganisms on the skin surface.
• Material selection: It is recommended to wear loose and soft cotton clothing and avoid materials such as wool and synthetic fibers that are easy to rub against the skin.
In daily care, the focus should be on keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding scratching, and seeking medical attention promptly. If a family member has an infectious skin disease (such as scabies or impetigo), separate clothing must be washed. With scientific care and appropriate protection, it is entirely possible to maintain normal family life while ensuring hygiene.


