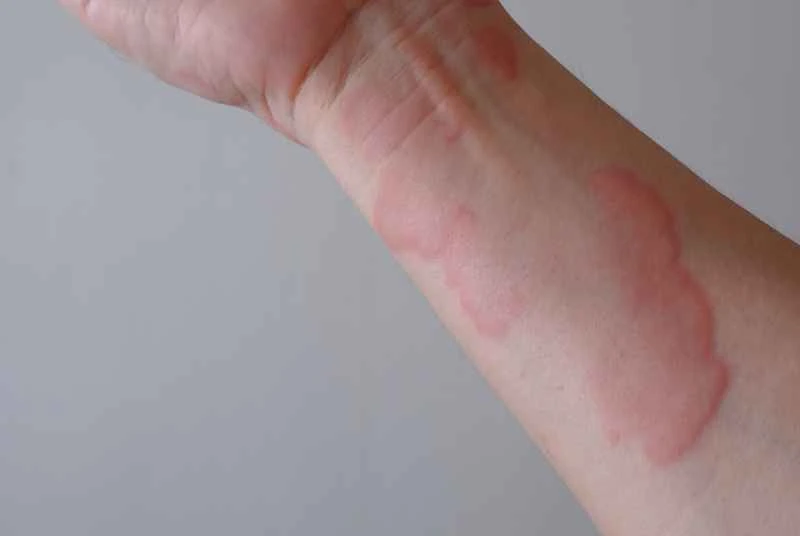
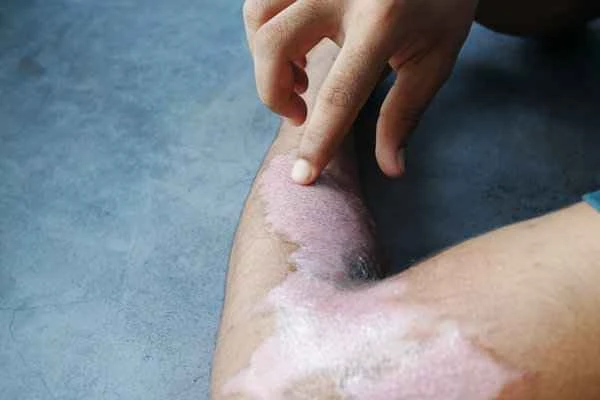
Urticaria itself is not contagious, so there is no such thing as a "contagious period." The duration of symptoms varies from person to person and usually subsides on its own within hours to days. Patients are advised to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and avoid scratching their skin.
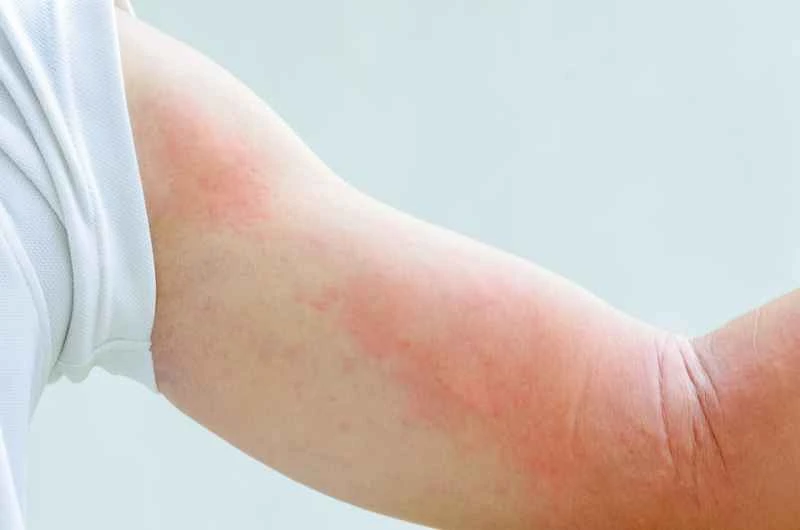
1. **Symptom duration varies greatly.**
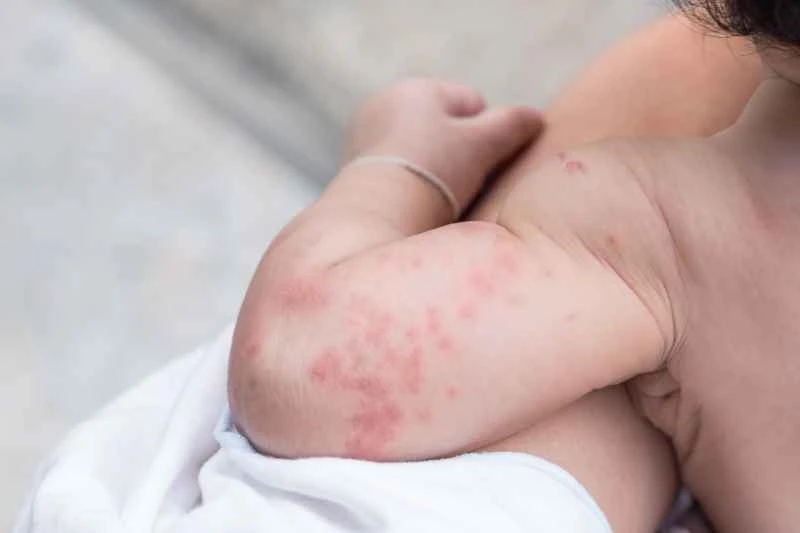
Acute urticaria may subside within hours or days, while chronic urticaria may recur for weeks or more. The specific duration depends on individual constitution and triggering factors, and cannot be generalized.
2. **The key lies in finding the trigger.**
Common triggers include food allergies, drug reactions, infections, or physical irritants. Recording changes in diet and environment before an attack can help doctors make a diagnosis.
3. **Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms.**
Doctors often prescribe anti-allergy medications to relieve itching and hives. Self-medication may mask the underlying cause; it's necessary to follow your doctor's instructions to adjust the treatment plan.
For daily care, it is recommended to wear loose-fitting cotton clothing, bathe with warm water, and avoid excessively hot environments that may irritate the skin. If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the eyelids or lips, seek medical attention immediately. Be patient; most cases of urticaria can be effectively controlled with proper management.