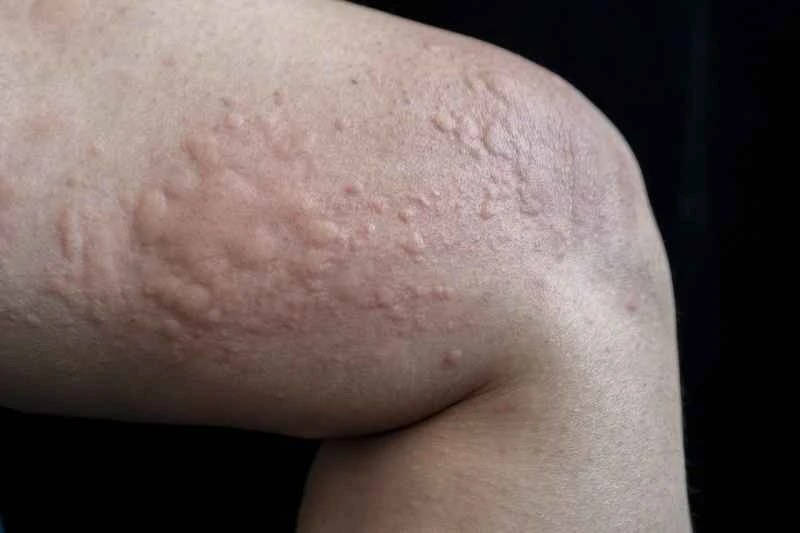
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that cannot be completely cured at present, but the condition can be effectively controlled through standardized treatment.
The pathogenesis of eczema is complex, involving multiple factors, including genetics, immune abnormalities, and environmental stimuli. Because its causes are difficult to completely eliminate, a complete cure is impossible. However, with proper treatment such as the use of antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, and avoidance of triggering factors, symptoms can be effectively relieved and the condition controlled. Regular follow-up appointments are recommended, along with attention to personal hygiene to prevent recurrence.
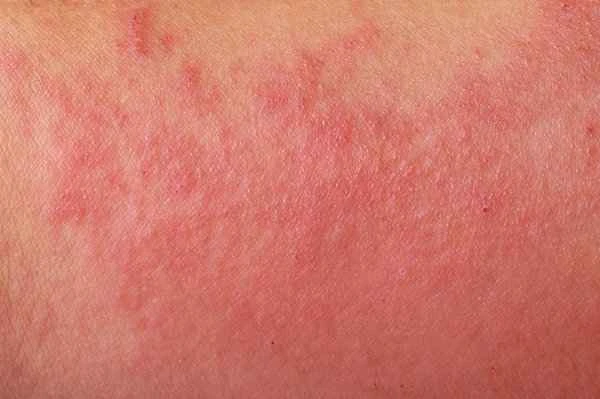
Eczema is usually not completely curable because its pathogenesis is complex and related to factors such as genetics, immune abnormalities, and environmental stimuli. Although the cause cannot be completely eliminated, the condition can be controlled through standardized treatment.
For eczema patients, keeping the skin clean and dry, wearing loose and breathable clothing, and avoiding excessive scratching are important measures to reduce symptom flare-ups. In addition, regular check-ups and adjustments to the treatment plan are also crucial.