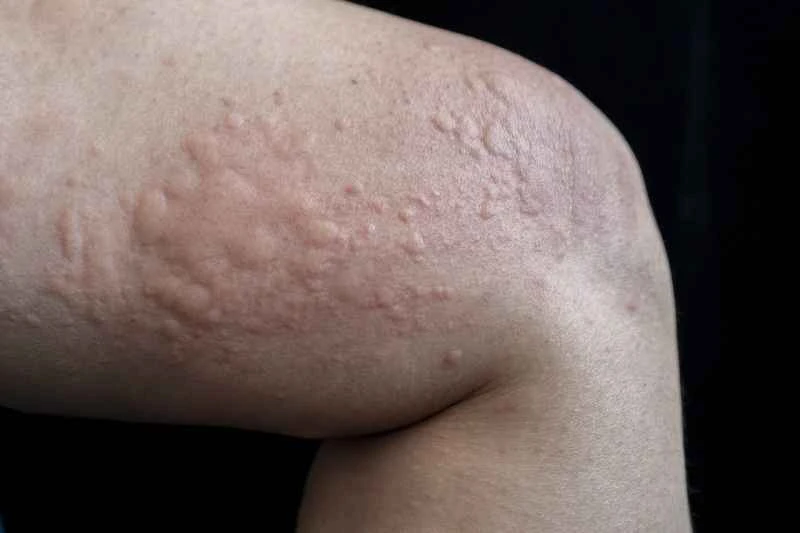
Treatment for urticaria usually requires selecting medication based on the specific symptoms and cause. No single medication is suitable for everyone; it is recommended to use medication under the guidance of a doctor. The following are common medication usage scenarios:
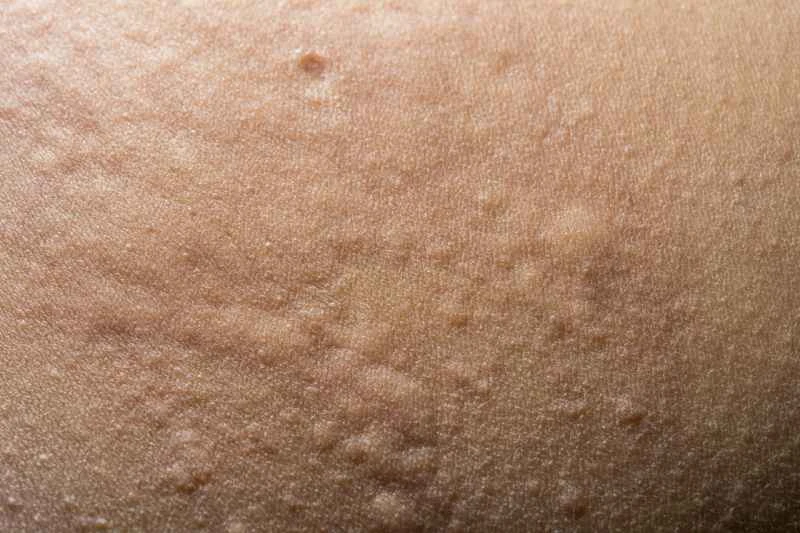
1. Relieve itching and redness: Commonly used antihistamines, such as loratadine and cetirizine, can help reduce hives and itching. Some medications may cause drowsiness, so pay attention to the timing of administration.
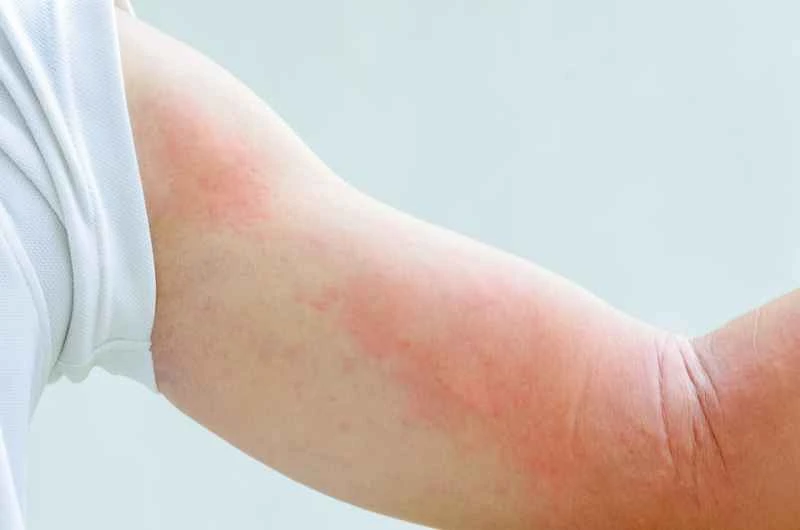
2. Controlling more severe symptoms: If symptoms are recurring or affect daily life, doctors may prescribe hormone medications for a short period of time, but the dosage must be strictly followed and long-term self-medication should be avoided.
3. Addressing special causes: If caused by infection or immune problems, treatment should target the underlying cause and combine with anti-allergy medications to improve skin symptoms.
Daily advice includes recording your diet, environment, and other factors that trigger an attack, and avoiding known allergens; wearing loose-fitting cotton clothing to reduce skin irritation. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly to adjust your treatment plan; do not arbitrarily change or discontinue medication.