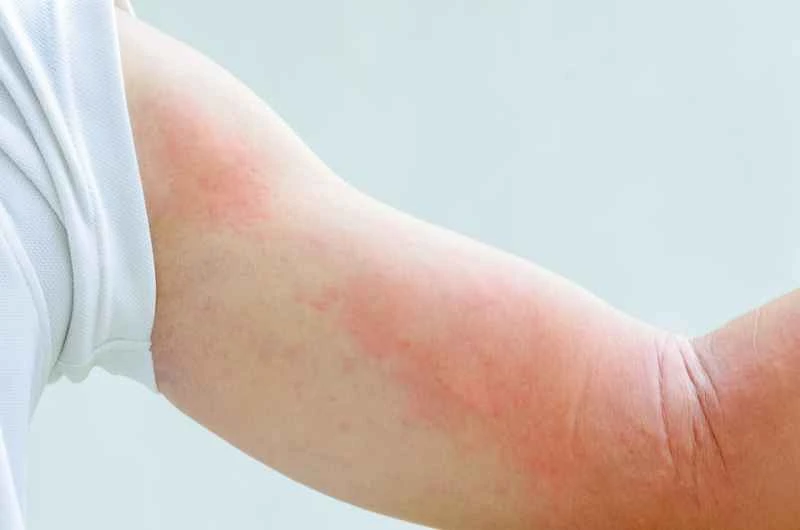
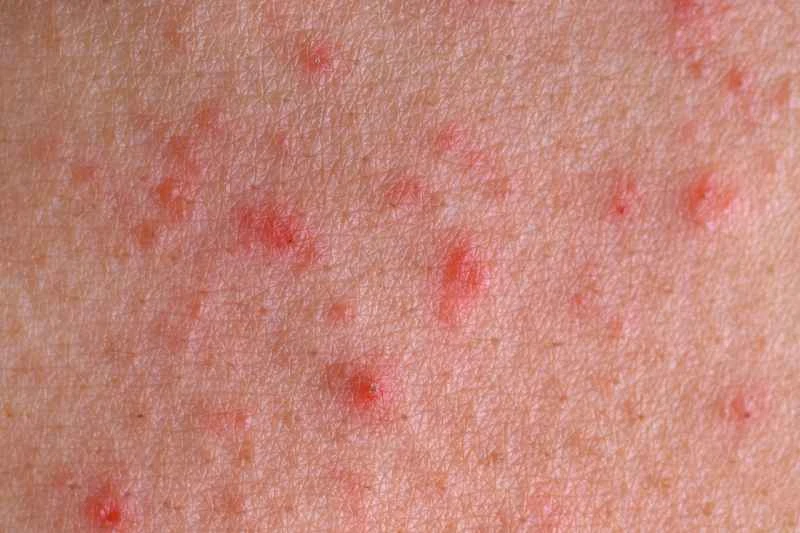
Urticaria is not contagious, so there's no need to worry about spreading it to others through daily contact. However, patients need to take care of themselves to alleviate symptoms and reduce recurrence.
1. Differentiate the cause and avoid triggers.
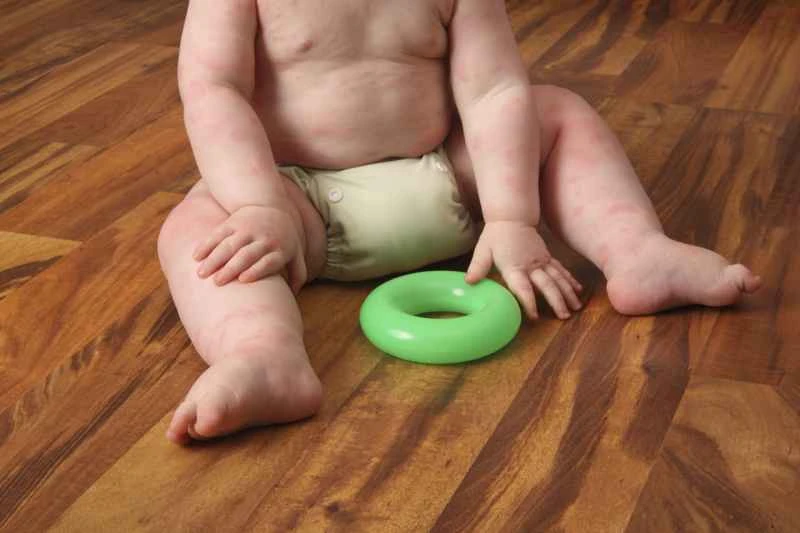

Urticaria is often caused by allergies, infections, or physical irritants. In daily life, you can pay attention to and try to avoid possible triggering factors, such as certain foods, medications, pollen, hot or cold stimuli, or excessive stress.
2. Use medication scientifically and treat according to standards.
If hives and itching occur, use anti-allergy medication under the guidance of a doctor. Do not adjust the dosage on your own or use folk remedies indiscriminately. If accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
3. Pay attention to daily skin care
During an flare-up, it is recommended to wear loose, soft cotton clothing to reduce friction. Bath water should not be too hot, and avoid using harsh bath products. Try to avoid scratching to prevent skin damage and infection.
4. Maintain healthy lifestyle habits
Getting enough rest, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and engaging in moderate exercise can help regulate immunity. A light diet is recommended, and keeping a food diary can help identify potential allergens.
In short, the key to managing urticaria is scientific management rather than excessive anxiety. Maintain a clean living environment, identify and avoid personal triggers, and follow your doctor's instructions for standardized treatment and regular check-ups. These measures will help you better control the condition.