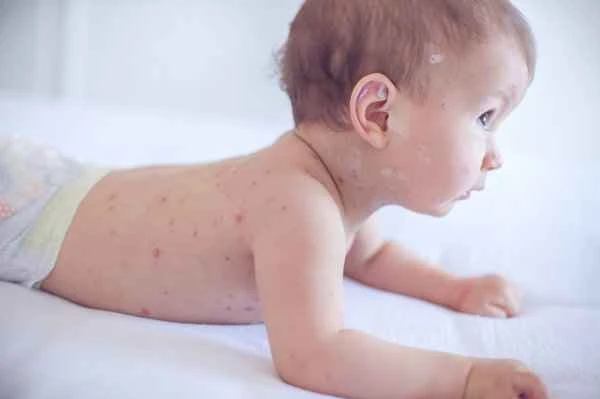
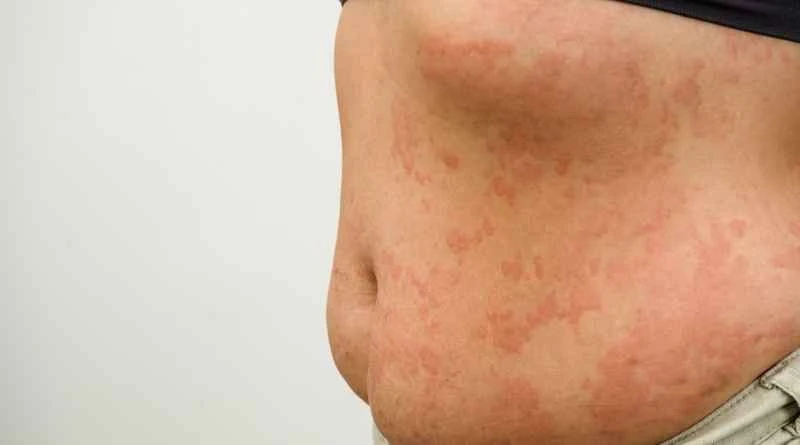
It is not contagious. Papular urticaria is a common allergic skin reaction, usually caused by insect bites or contact with allergens, and is not transmitted from person to person through contact or air. If you or a family member develops symptoms, there is no need to worry about infecting others, but you should take care to avoid recurring flare-ups.
Specifically, this can be understood from the following aspects:

1. The cause is not related to infection: This disease is mainly caused by an individual's allergy to substances such as insect saliva and mites. It is an autoimmune reaction, similar to someone being allergic to pollen. However, the allergy itself is not contagious.
2. Although the symptoms are similar to an infection, they are different in nature: Red papules or blisters on the skin may be mistaken for "infectious skin diseases", but in fact these rashes are local allergic reactions and will not be transmitted to others through sharing items or skin contact.
3. Cases with frequent family outbreaks: If family members become ill at the same time, it is usually because they are exposed to the same environment (such as mosquito breeding grounds or dust mite environments) rather than because they are infected with each other.
It is recommended to keep your living environment clean to reduce mosquito breeding; use mosquito repellent when outdoors; if the rash worsens or is accompanied by fever, seek medical attention promptly to rule out other possibilities. Avoid scratching the rash to prevent secondary bacterial infection.