While hives generally don't directly affect the menstrual cycle, they can indirectly disrupt a woman's menstrual cycle. If menstrual irregularities occur, it's recommended to first rule out gynecological or endocrine causes, and at the same time, manage allergy symptoms.
This can be understood from the following two aspects:
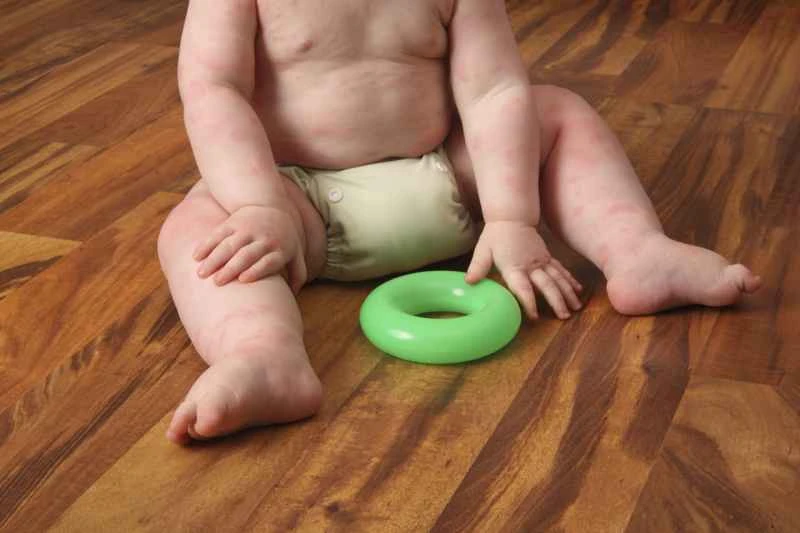

1. Physical stress may indirectly interfere with menstruation: When urticaria occurs, persistent itching, poor sleep quality, or anxiety may put the body in a state of tension. This stress can sometimes temporarily affect hormone levels, causing slight fluctuations in the menstrual cycle.
2. Cautions regarding medication use: Some medications used to relieve urticaria (such as certain antihistamines or hormones) may have a slight effect on the endocrine system. If menstrual changes occur after taking the medication, consult a doctor to see if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted.
Women are advised to keep track of their menstrual cycle changes during an urticaria flare-up and avoid excessive scratching to prevent infection. If menstruation is irregular for a prolonged period or accompanied by severe discomfort, they should seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and managing emotional stress can also help stabilize the menstrual cycle.