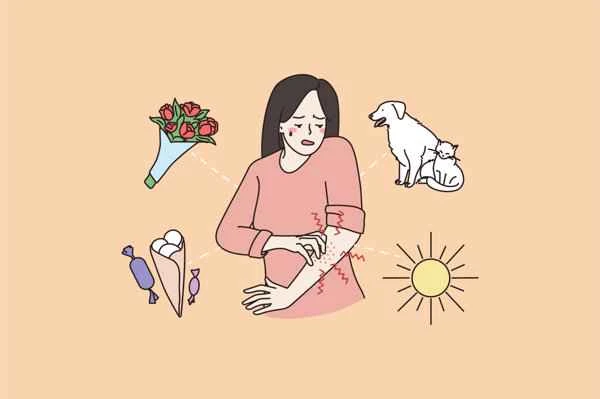
Recovery time for urticaria varies from person to person. Acute flare-ups usually subside on their own within hours to weeks, while chronic cases may last for months or even longer. It is recommended to closely monitor changes in symptoms and consult a doctor if necessary.

1. Acute urticaria: Most cases are caused by allergies or infections. Symptoms such as wheals and itching may appear suddenly, but usually subside within 24 hours and disappear on their own after several days to two weeks. If it recurs frequently, the trigger should be investigated.
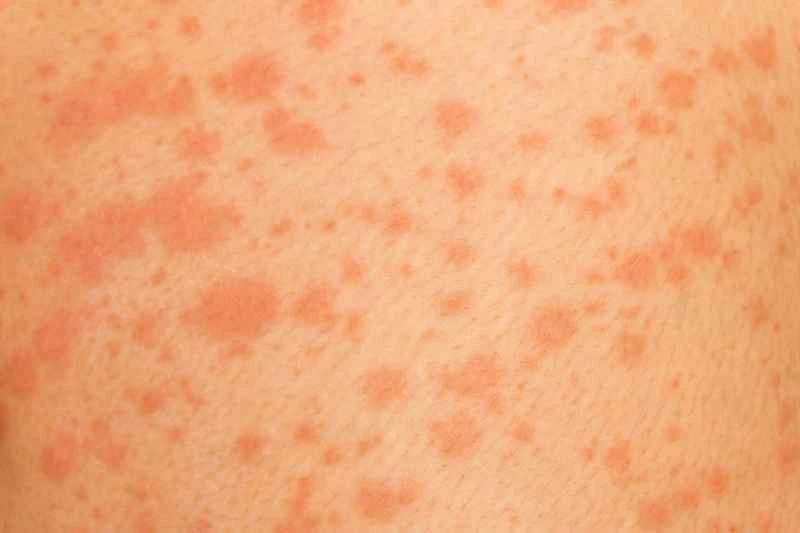
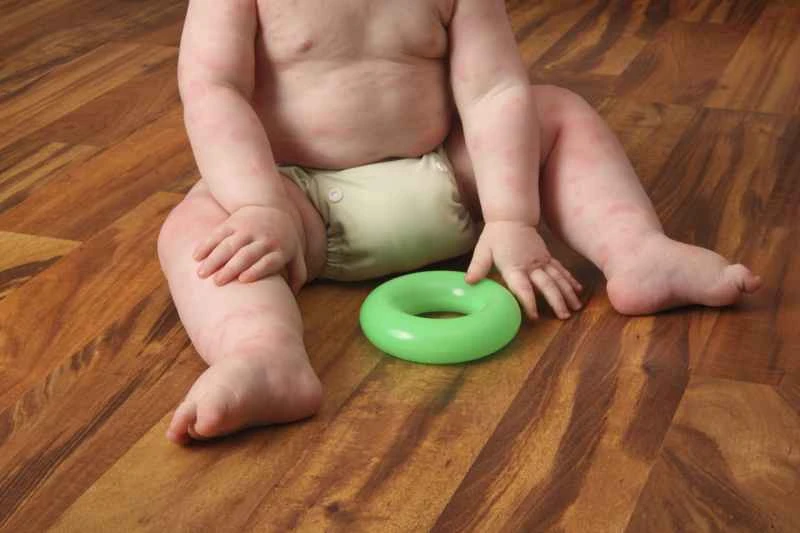
2. Chronic urticaria: If symptoms occur more than twice a week and last for more than 6 weeks, spontaneous recovery is slow. This may be related to factors such as immunity and stress, and requires a longer period of treatment.
3. Influencing factors: Recovery speed is affected by individual constitution, whether the triggering factor persists, and care methods. For example, avoiding contact with allergens and reducing scratching can help speed up recovery.
In daily life, you can keep a record of changes in your diet and environment to identify triggers, and wear loose clothing to reduce irritation. If symptoms become frequent or worsen, it is recommended to see a doctor for examination; the doctor may recommend medication depending on the situation. Be patient and gradually adjust your lifestyle habits, which will help your body recover naturally.