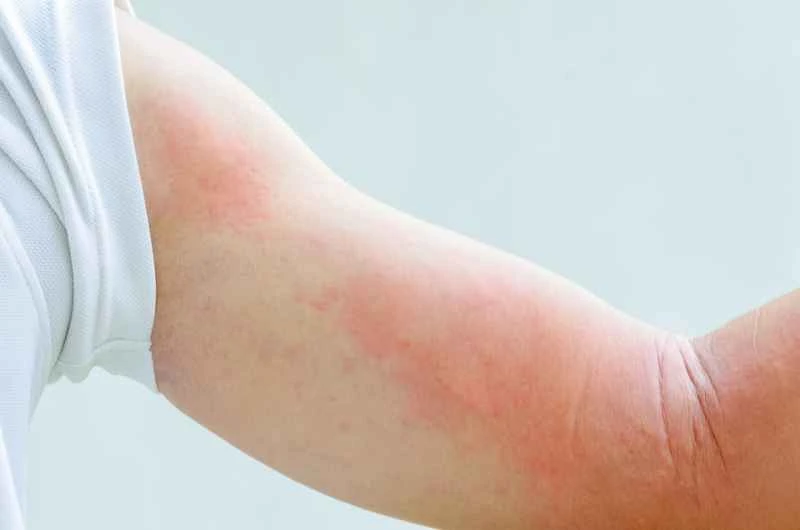
Urticaria is usually triggered by allergic reactions or bodily sensitivities. Male patients can effectively control their symptoms with proper treatment. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to identify the underlying cause and manage the condition long-term under the guidance of a doctor.
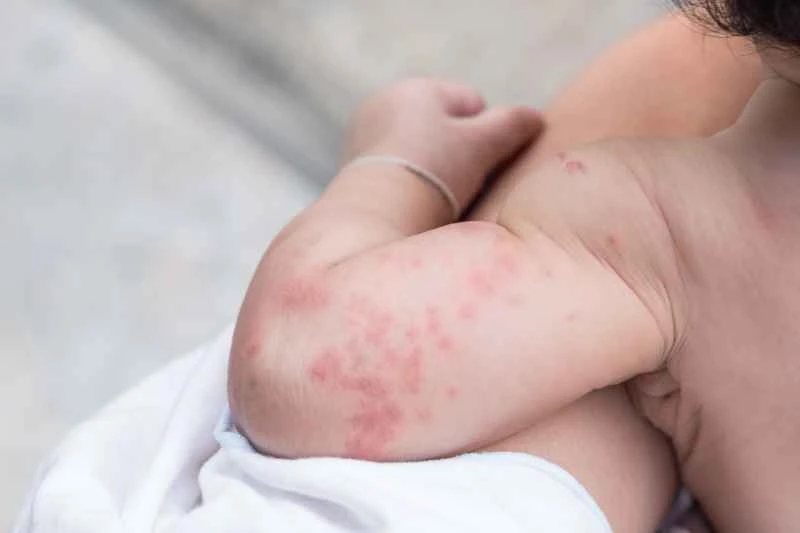
1. Common triggering factors
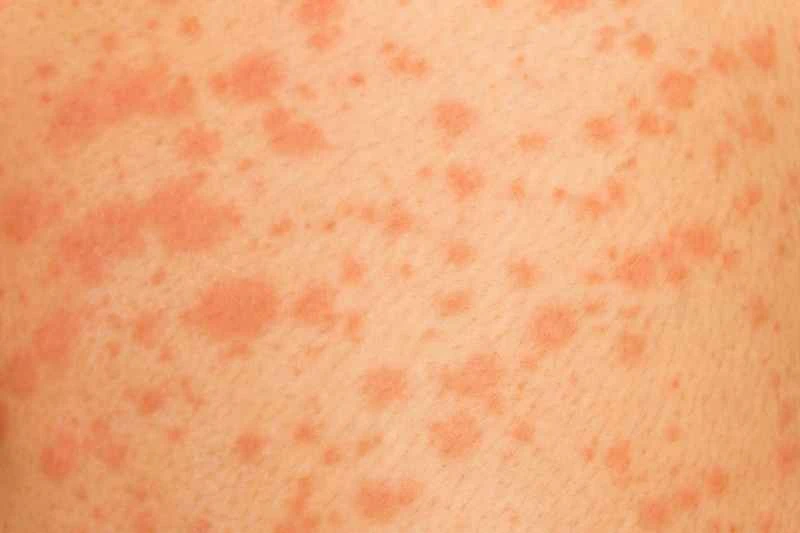
Exposure to allergens such as pollen and dust mites, consumption of seafood or medications, as well as infections and stress, can all trigger dilation of blood vessels in the skin, resulting in red, swollen, and itchy wheals. Men, with their wider range of daily activities, are more likely to be exposed to a variety of environmental factors.
2. Treatment and Management Methods
Most patients can relieve their symptoms with antihistamines. Doctors will advise avoiding known triggers and using topical ointments to alleviate discomfort, depending on the situation. When flare-ups recur, it's important to keep a record of daily life details to help identify potential triggers.
3. Disease course and prognostic characteristics
Some acute flare-ups subside gradually after the triggering factor is eliminated, while chronic urticaria may require a longer period of management. Patience and regular follow-up appointments help adjust the treatment plan and reduce the frequency of recurrence.
Male patients are advised to wear loose-fitting cotton clothing and avoid overheated environments that may irritate the skin. Daily records of diet and activity can help doctors analyze the cause. If symptoms suddenly appear and are accompanied by difficulty breathing, immediate medical attention is necessary.