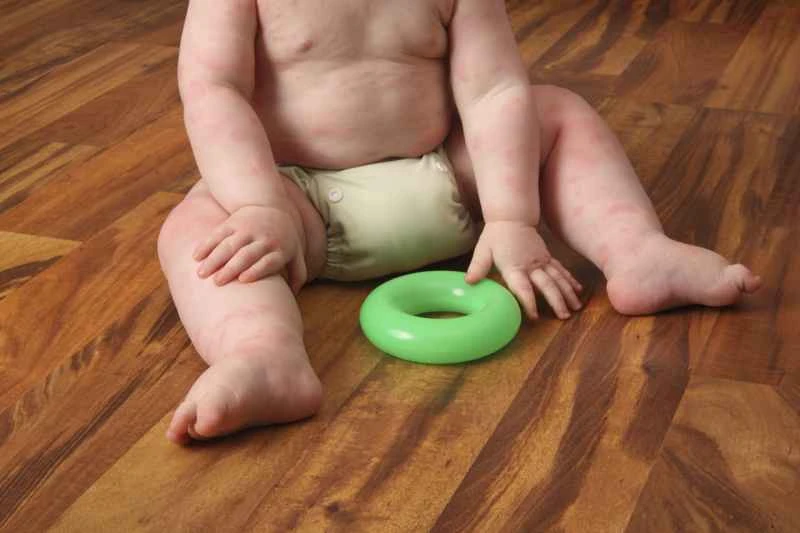
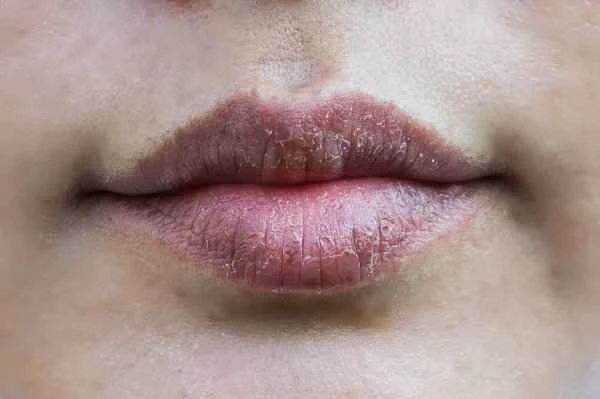
It is not contagious. Eczema is a skin condition, not caused by bacteria or viruses, and therefore cannot be transmitted from one person to another through contact. Parents can rest assured that their children will not infect others when playing with family and friends. However, eczema-affected skin requires careful care to prevent scratching that could break the skin and lead to other infections.
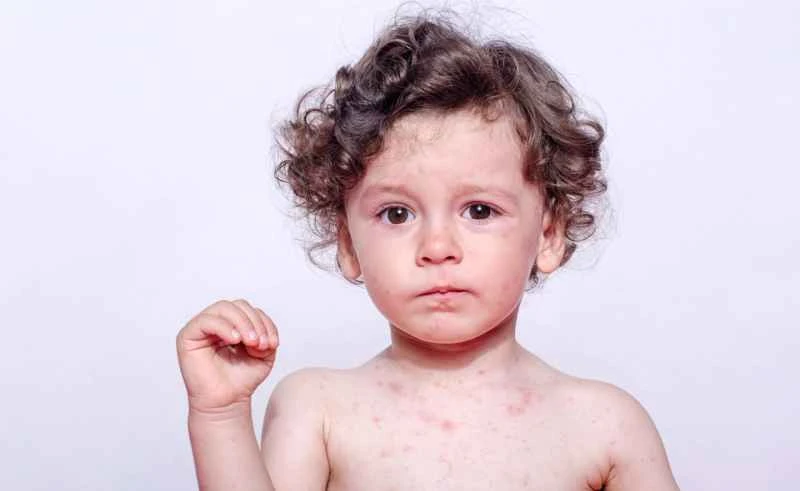
Specifically, this can be understood from the following aspects:
1. **The root cause of eczema lies internally:** It is usually related to a weak skin barrier function, allergic constitution, or environmental stimuli. It is an internal reaction of the body, just like some people are prone to food allergies. It is not a "contagious disease".
2. **Symptoms may be misleading:** When eczema flares up, the skin becomes red, develops rashes, and sometimes oozes fluid, which may look alarming and lead people to mistakenly believe it is contagious. However, this is simply a manifestation of skin inflammation and is not contagious in itself.
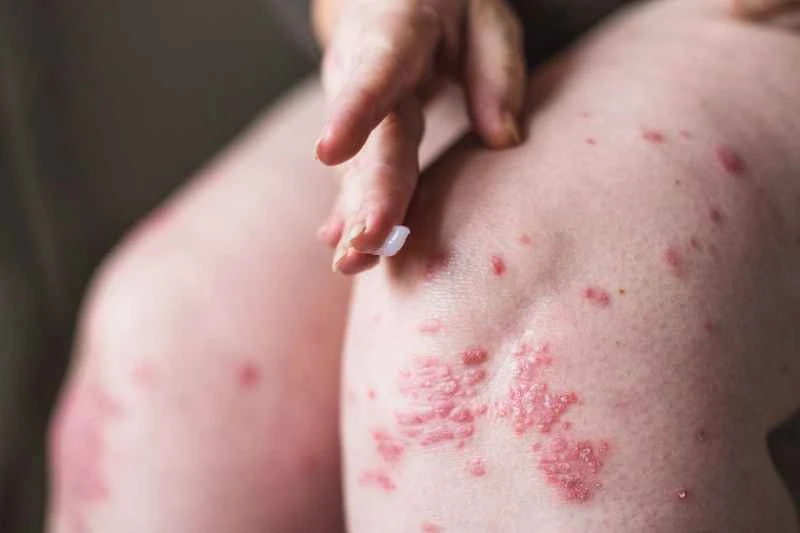
3. **Secondary infections need to be monitored:** Although eczema is not contagious, scratching broken skin can allow bacteria to enter and cause local infection. In this case, the infection is caused by bacteria, not by the eczema itself.
To make your child more comfortable, it's recommended to first focus on moisturizing their skin, applying a gentle moisturizing cream several times a day. Secondly, avoid dressing your child in too many layers or using harsh bath products. If the eczema is severe or recurring, consult a doctor promptly for guidance on care or medication to help control the condition.