Medication for childhood urticaria should be chosen under the guidance of a doctor. Antihistamines are usually used, but the specific medication should be determined based on age, severity of symptoms, and doctor's assessment. Do not self-medicate.

1. **Common Drug Types**
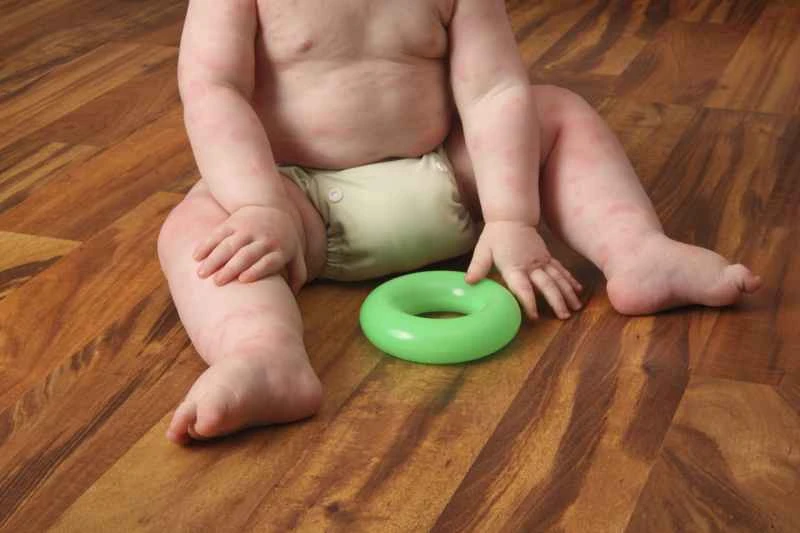

Second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine, are commonly used in children. These medications may help relieve itching and hives and have relatively few side effects. Some infants and young children may require dosage adjustments based on their weight.
2. **Differences in Age and Medication Use**
Medication use differs for children of different ages: children over 2 years old can usually use oral antihistamines under the guidance of a doctor; medication use for infants under 2 years old requires extra caution and must be prescribed by a doctor based on the specific circumstances.
3. **Precautions**
Observe your child's reaction during medication. If drowsiness, dizziness, or other discomfort occurs, consult a doctor promptly. Avoid using medication ingredients that may cause allergies, and follow care measures such as avoiding scratching and keeping the skin clean.
If a child develops hives, it is recommended to consult a doctor to determine the cause and develop a suitable medication plan. Daily monitoring of diet and environmental factors during flare-ups, avoiding contact with known allergens, and keeping the skin moisturized can help reduce symptom recurrence.