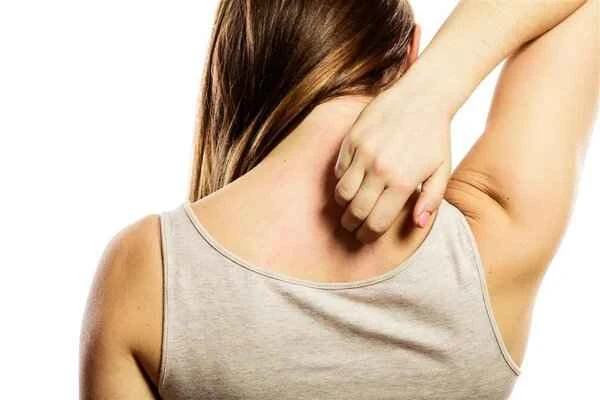
No. Urticaria itself is not contagious to others through contact or daily interactions, but it is important to avoid shared triggers and pay attention to your partner's health.
1. **The difference between etiology and transmission**
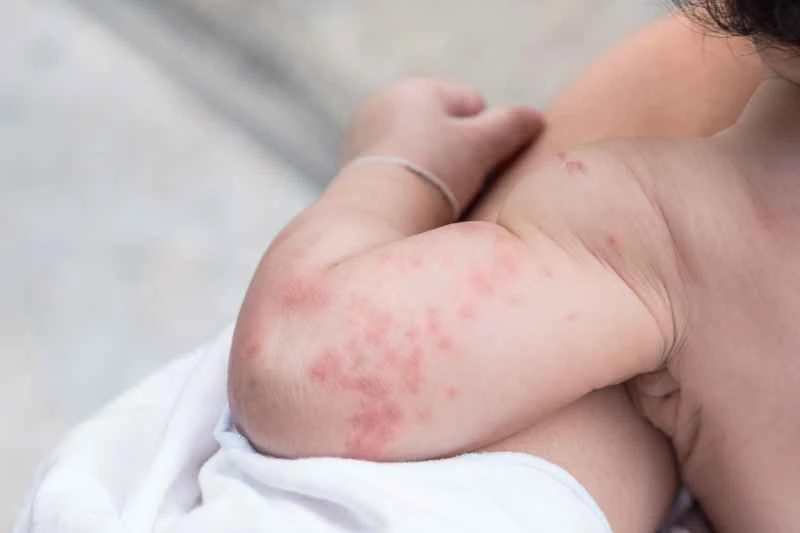
Urticaria is usually triggered by allergies, infections, or internal factors, and is an autoimmune response, unlike colds or skin diseases which are transmitted directly through bacteria or viruses. Even if a partner develops a similar rash, it is likely due to exposure to the same allergen (such as food or pollen), rather than transmission between partners.
2. **Special Circumstances Requiring Attention**
If urticaria is triggered by certain infections (such as viral colds), the infection itself may be contagious, but the rash symptoms will not spread directly. In this case, attention should be paid to personal hygiene to avoid cross-infection.
3. **Points to Note in Daily Interactions**
When living together, help your partner keep track of factors that may trigger rashes (such as diet and environmental changes) and reduce exposure to known allergens. If your partner develops skin problems, it is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause, rather than attributing it to "contagion."
If you or your partner experience recurring rashes, it is recommended that you work together to identify potential triggers in your living environment and consult a doctor separately. Maintaining healthy lifestyle habits and keeping a dietary record can help reduce the occurrence of symptoms.