Heat urticaria is an acute skin reaction triggered by heat stimulation. The key to treatment is rapid symptom relief and control of flare-ups. The core of treating heat urticaria is avoiding triggering factors such as high temperatures and strenuous exercise, while using antihistamines to relieve itching and redness. These medications reduce inflammation by blocking the action of histamine, thus achieving rapid relief. Topical cold compresses can quickly lower skin temperature and alleviate symptoms, while avoiding hot baths and prolonged exposure to high temperatures are also important measures for controlling flare-ups.
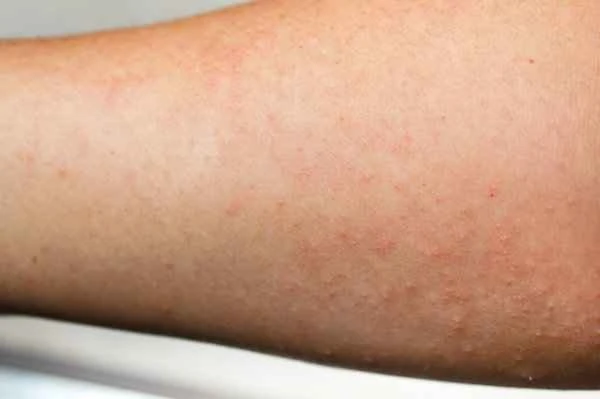
When treating urticaria, special attention needs to be paid to potential risks and common misconceptions. Some patients may mistakenly believe that all antihistamines are equally effective; in reality, different types of antihistamines vary in the speed and duration of symptom relief. Over-reliance on medication while neglecting the importance of avoiding triggers can lead to recurrent symptom attacks. During treatment, a comprehensive approach combining medication and lifestyle modifications should be considered to achieve the best therapeutic effect.
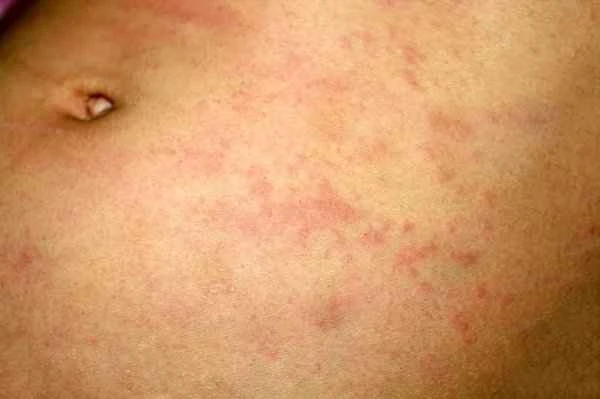
[Management Tip:]

1. Avoid high-temperature environments and strenuous exercise to reduce heat stimulation.
2. Use non-sedating antihistamines, such as cetirizine, to quickly relieve symptoms.
3. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly and consult a professional doctor.