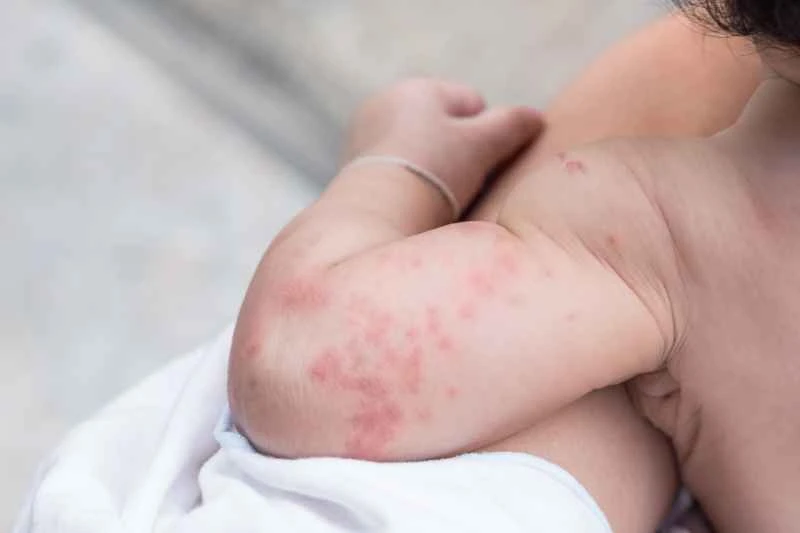
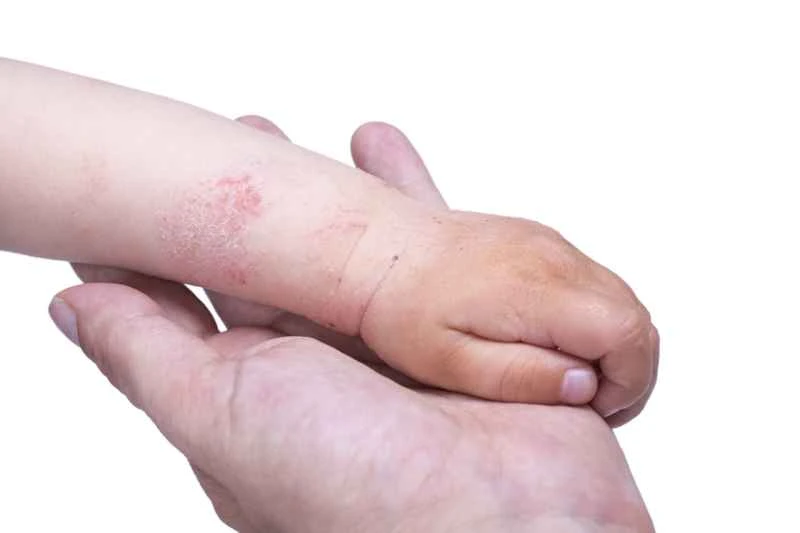
The choice of ointment for seborrheic dermatitis should be based on the severity of the dermatitis and the individual's specific situation. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition, mainly characterized by excessive sebum secretion, leading to symptoms such as erythema and scaling. When treating seborrheic dermatitis, the choice of ointment should consider factors such as the severity of the dermatitis, the patient's skin type, and the presence of infection.
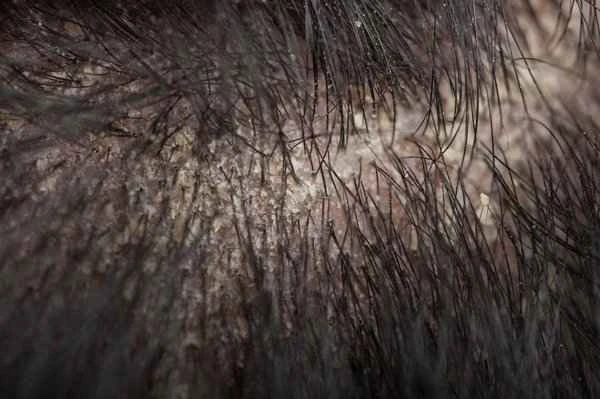
Medications for treating seborrheic dermatitis are mainly classified into several types, including antifungal creams, corticosteroid creams, and anti-inflammatory creams. Antifungal creams, such as ketoconazole, can effectively inhibit the growth of fungi that cause seborrheic dermatitis, thereby relieving symptoms. Corticosteroid creams, such as hydrocortisone, have strong anti-inflammatory effects and can reduce redness and itching caused by dermatitis. Anti-inflammatory creams, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can relieve the inflammatory response caused by dermatitis and alleviate symptoms. The selection and use of these creams should be based on the patient's specific condition and guided by a doctor to ensure safety and effectiveness.

When treating seborrheic dermatitis, in addition to choosing a suitable ointment, it's important to avoid some common misconceptions. Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis requires long-term adherence; you shouldn't stop using the ointment just because symptoms improve temporarily. Treatment involves more than just topical medications; it also requires attention to daily skin care, such as keeping the skin clean and avoiding the use of harsh cleansers. Finally, treatment for seborrheic dermatitis needs to be individualized. Different patients have different conditions and skin types, so the choice and use of ointments must be adjusted according to individual circumstances.

[Management Tips]
1. Choose the appropriate ointment according to the doctor's instructions, and pay attention to the method and frequency of use.
2. Pay attention to daily skin care, keep your skin clean, and avoid using harsh cleansing products.
3. Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor the recovery of dermatitis and adjust the treatment plan as needed.