The removal of raised scars involves a variety of methods to improve the appearance of the skin and restore its smoothness.
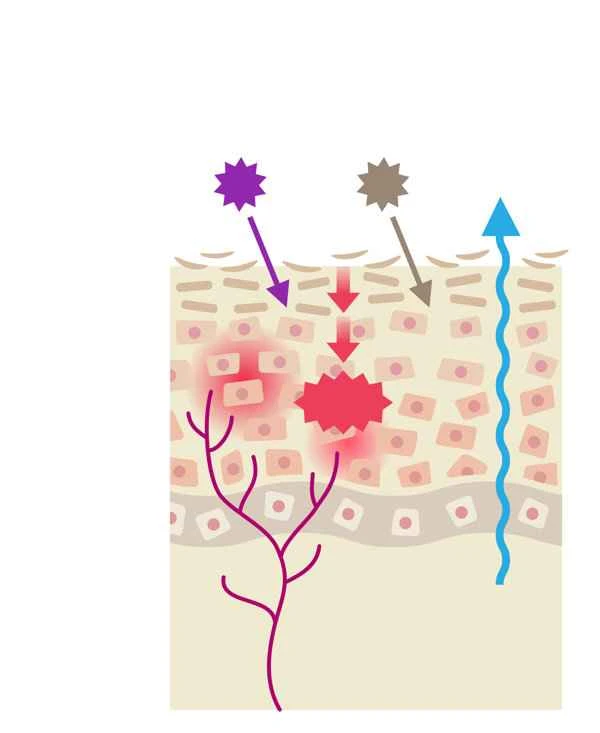
Raised scars, also known as atrophic scars or depressed scars, are usually caused by insufficient production of collagen and elastin fibers during the healing process after skin injury. These scars are common on skin after acne, trauma, or surgery. Methods for eliminating raised scars include non-surgical and surgical treatments. Non-surgical treatments mainly include laser therapy, microneedling, chemical peels, and dermal filler injections. Laser therapy can stimulate the skin to produce new collagen, improving the appearance of the scar; microneedling uses tiny needles to stimulate the skin and promote collagen production; chemical peels use chemicals to remove the epidermis, promoting skin regeneration; and dermal filler injections fill in the depressed areas, making the skin surface smoother. Surgical treatments include subcutaneous excision and subcutaneous excision combined with flap transfer, which directly remove scar tissue surgically, followed by skin repair.
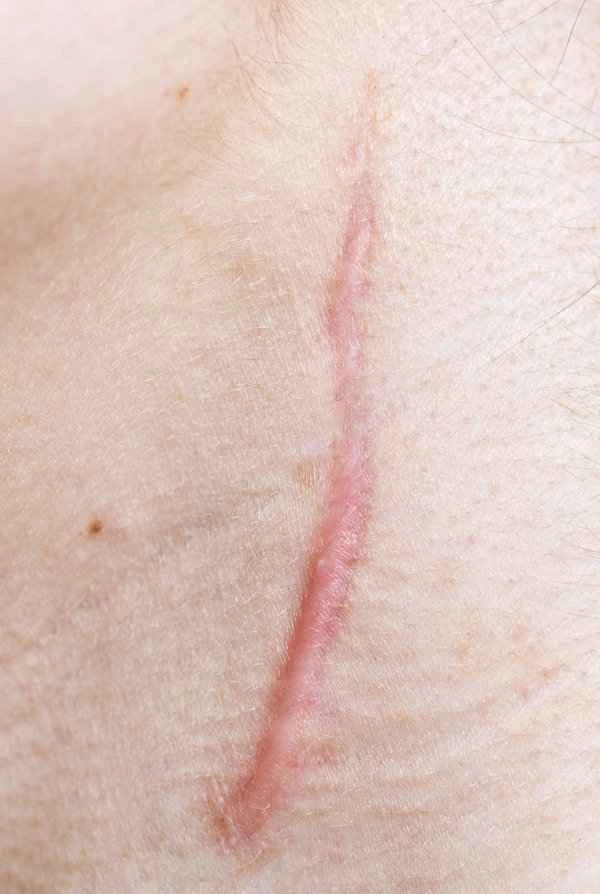
During the treatment of raised scars, patients may encounter some risks and misconceptions. Treating raised scars takes time and is not an overnight process; therefore, patients need patience and should not expect immediate, significant results. Different treatment methods are suitable for different types of scars, so choosing the appropriate treatment method is crucial. Finally, some side effects may occur during treatment, such as skin redness, swelling, and infection. Therefore, it is necessary to closely monitor the skin's reaction during treatment and communicate with the doctor promptly.
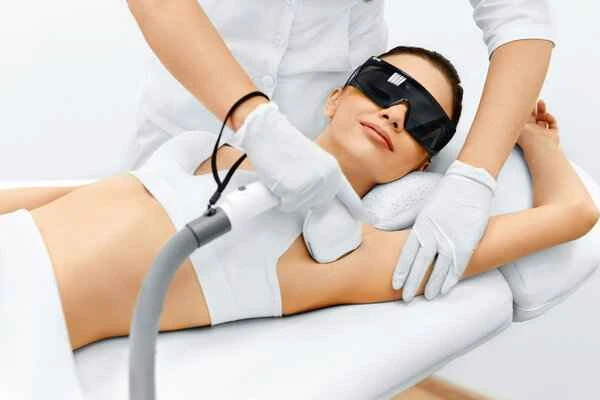
[Management Tip:]
1. Have regular skin checkups to detect and treat new scars promptly.
2. Maintain good skin care habits and avoid skin damage.
3. Seek medical attention promptly if infection or other adverse reactions occur.


